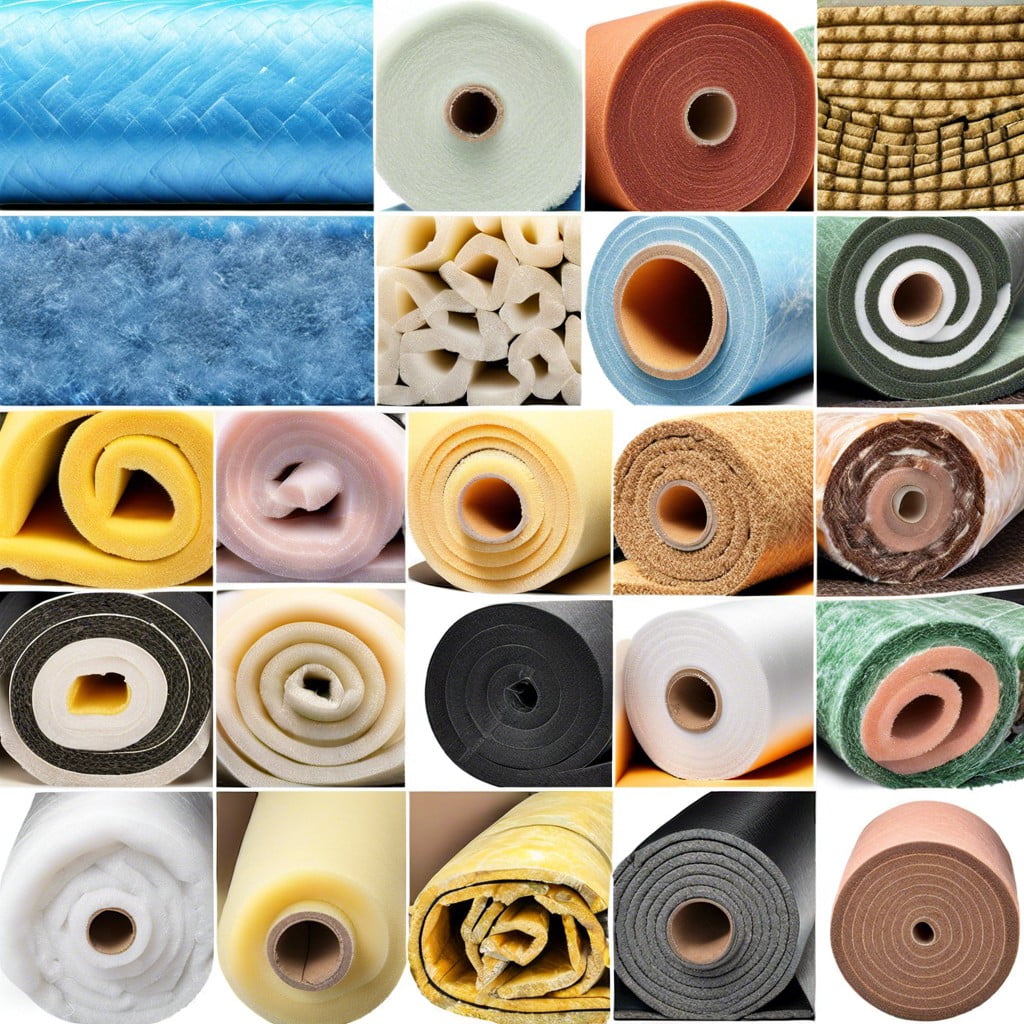
Here are the main types of polymer insulation used in construction. Discover their properties, benefits, and drawbacks.
Polymeric insulation materials are gaining widespread attention for their functionality and efficiency in various applications. These insulations typically consist of a polymer matrix and fillers, forming a highly effective barrier against thermal and electrical conductivity.
Polymers’ versatility and lightweight nature make them ideal candidates for creating advanced insulation systems that outperform traditional materials, such as glass or porcelain.
A variety of polymer-based insulations are available, which can be fine-tuned according to the specific needs of an application.
Some common types of polymeric insulators include polymer nanocomposites and polymer-based nano-composites for thermal insulation. These insulators improve overall performance by augmenting properties such as thermal stability, mechanical strength, and resistance to environmental factors like moisture or ultraviolet radiation.
As innovations in the field of materials science continue to progress, polymeric insulation will likely play an increasingly important role in meeting the demands of both conventional and emerging industries.
Researchers and engineers are continuously exploring new ways to optimize the performance of these insulators, leading to exciting advancements and promising future applications.
Key takeaways:
- Polymer insulation materials have a variety of types, including EPS, XPS, PIR, and polyurethane foam.
- Each type of polymer insulation has its own benefits and drawbacks.
- Polymer insulation offers advantages such as lightweight, cost-effectiveness, and good thermal performance.
- Factors to consider when choosing polymer insulation include R-value, heat transfer, air leakage, and temperature control.
- Advances in polymer insulation include nanotechnology, sustainable materials, smart insulation systems, aerogel-based insulation, and advanced manufacturing techniques.
Common Types of Polymer Insulation

Expanded Polystyrene (EPS)
Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) is a versatile and cost-effective insulation material commonly used in various construction applications. It is made from expanded polystyrene beads bonded together to form rigid boards or panels. EPS offers excellent thermal insulation properties and is typically lightweight, allowing for easy handling and installation. Its low-cost nature makes it a popular choice for residential and commercial projects.
- Pros: Lightweight, cost-effective, good thermal performance.
- Cons: Not as resistant to moisture as other materials.
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS)
Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) insulation is similar to EPS but has a more uniform structure that provides improved durability and moisture resistance. XPS is manufactured through an extrusion process, producing rigid foam boards with a closed-cell structure. This makes XPS more suitable for applications subjected to high levels of moisture, such as foundation walls or below-grade insulation.
- Pros: Enhanced durability, moisture resistance, suitable for various applications.
- Cons: More expensive than EPS.
Polyisocyanurate (PIR)
Polyisocyanurate (PIR) is a high-performance polymer insulation material that offers superior thermal insulation properties compared to EPS and XPS. PIR is manufactured as rigid foam panels with a closed-cell foam structure. The excellent thermal performance of PIR makes it an ideal choice for applications requiring high thermal resistance, such as roofs, walls, and floors.
- Pros: Superior thermal performance, durable, closed-cell structure.
- Cons: Higher cost than EPS and XPS.
Polyurethane Foam
Polyurethane foam is a versatile and highly efficient insulating material that provides excellent thermal and acoustic insulation. It is available as both rigid panels and as a spray-applied foam, allowing for a wide range of applications. Polyurethane foam can be used to insulate walls, roofs, and floors, among other areas.
- Pros: High thermal and acoustic insulation, adaptable to multiple applications.
- Cons: May be more expensive than other insulation types, susceptible to moisture.
Open-Cell and Closed-Cell Insulation
Polymer insulation can be classified as either open-cell or closed-cell based on its structure. Open-cell insulation has a less dense and interconnected cell structure, while closed-cell insulation is composed of tightly-packed individual cells. Open-cell insulation is generally lightweight and provides good sound absorption, whereas closed-cell insulation tends to have superior moisture resistance, strength, and R-value.
- Open-Cell Pros: Lightweight, good sound absorption, less expensive.
- Open-Cell Cons: Lower R-value, less moisture resistance.
- Closed-Cell Pros: High R-value, moisture resistance, dimensional stability.
- Closed-Cell Cons: More expensive, less sound absorption.
Thermal Performance and Energy Efficiency
R-Value
The R-value is a measure of thermal resistance, which indicates a material’s effectiveness in insulating against heat transfer. Higher R-values represent better insulation.
Polymer insulations, such as polypropylene nonwoven fabrics, have different R-values than traditional insulations like fiberglass or mineral wool. Factors that affect the R-value of polymer insulations include material composition and thickness.
Heat Transfer
Heat transfer in insulation materials occurs through conduction, convection, and radiation. Polymer insulation materials usually have lower thermal conductivities than inorganic materials, which means they are generally less effective at conducting heat.
However, some advanced polymer insulations, such as composite structural insulated panels consisting of glass fiber reinforced polymer and cementitious materials, have improved heat transfer characteristics and enhanced energy behaviors compared to traditional insulation materials.
Air Leakage
Air leakage is a vital factor in the overall thermal performance of an insulation material. Sealing gaps and cracks helps prevent air leaks and contributes to energy efficiency. Polymer insulations can be designed with tight seals to minimize air leakage, consequently reducing energy bills.
Temperature Control
Effective temperature control is critical for maintaining comfort in a building and reducing energy costs. Some polymer insulation materials, including additively manufactured polymer lattices, offer thermal performance that allows for better temperature control and energy efficiency in various applications.
Overall, the thermal performance and energy efficiency of polymer insulations depend on factors such as R-values, heat transfer capabilities, air leakage prevention, and temperature control. By considering these aspects, one can make informed decisions on choosing the right polymer insulation material for their specific needs.
Applications and Installation Methods

Foam Board
Foam board insulation is commonly used in a variety of construction projects due to its insulating properties. It is typically made from polystyrene, polyisocyanurate, or polyurethane materials and can be installed in walls, floors, and roofs.
Foam board provides a high insulating value and is less expensive and easier to install than some other insulation types. Its applications include residential and commercial buildings, insulating ducts, and attenuating sound.
Blown-In Insulation
Blown-in insulation, often made from fiberglass or cellulose materials, is an effective method to insulate hard-to-reach areas such as attics and wall cavities. It is applied by using a machine that blows loose-fill insulation into the desired space.
This method not only provides excellent thermal insulation but also creates an air barrier, which reduces heat loss and improves energy efficiency. Suitable applications include retrofitting existing homes and improving poorly insulated buildings.
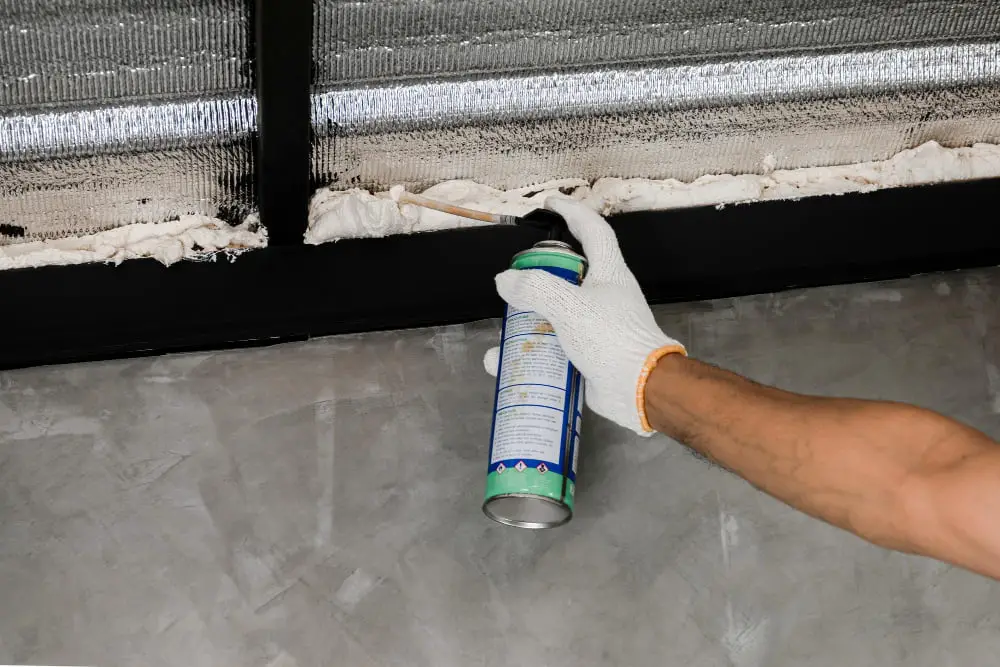
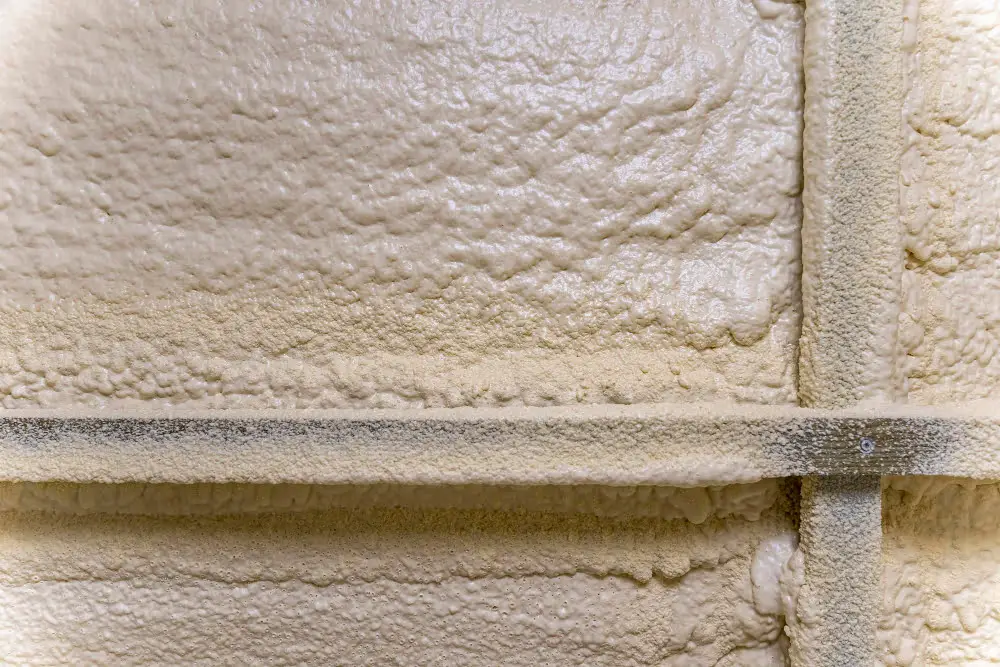
Sprayed Foam and Foamed-In-Place
Sprayed foam insulation, such as polyurethane foam, is a two-component mixture that is applied using specialized equipment to create a seamless insulation layer. Foamed-in-place insulation is another variant of sprayed foam, where the foam is applied directly onto surfaces like walls and floors.
These types of insulation provide excellent thermal insulation, reduce air infiltration, and can be used to fill irregular spaces. Common applications include insulating concrete block walls, rim joists, and attic spaces in both residential and commercial buildings.
Concrete Block Insulation
Concrete block insulation includes a variety of methods for insulating concrete blocks used in construction projects. Some of these methods include insulating concrete forms (ICFs), structural insulated panels (SIPs), autoclaved aerated concrete (AAC), and autoclaved cellular concrete (ACC).
These types of insulating blocks not only add thermal efficiency to walls but also can offer structural strength when used in conjunction with other building materials.
Concrete block insulation is appropriate for the construction of homes, commercial buildings, and industrial facilities, and it can improve the energy efficiency, comfort, and durability of a building.
Environmental Impact and Sustainability

Recycled Plastics in Insulation
Recycled plastics, such as PET bottles, can be effectively used in the production of thermal insulation panels, reducing the environmental impact associated with the extraction and production of raw materials.
A study shows that by recycling post-consumer PET bottles into polyester fibers, it is possible to create eco-sustainable materials that contribute to greenhouse gas emissions reduction. After careful selection of plastic waste by type and polymer, these materials can be successfully incorporated into building insulation products.
Sustainable Construction
The use of sustainable biocomposites in building insulation materials contributes to lowering the environmental impact of construction. An example is the development of thermal insulation biocomposites made from rice husk, wheat husk, wood fibers, and textile waste fibers.
These biodegradable materials are mixed with biodegradable polymers to enhance their toughness while preserving their environment-friendly properties. Incorporating such materials into building envelopes can help reduce the embodied environmental impact of green buildings.
Greenhouse Gas Emissions
Minimizing the embodied environmental impact of building insulation is essential for achieving a smaller carbon footprint. To achieve this, automatic optimization methods can be applied to assess the environmental performance of various insulation materials and configurations. One such strategy includes evaluating polymer-based thermal insulation materials for their greenhouse gas emissions potential during production and disposal.
Using sustainable, recycled plastics and biocomposites as insulation materials can reduce the carbon footprint of buildings and contribute to a more sustainable future.
When selecting insulation materials, considering their environmental impact is essential in the decision-making process.
Advantages and Considerations
Lightweight and Durable
One of the main advantages of polymer insulation is that it is both lightweight and durable. This property makes it an attractive option for homeowners who are looking for an energy-efficient insulation material.
Polymer insulation materials, such as silicone, are known for their durability and robust performance in outdoor applications. As a result, they can effectively withstand harsh environmental conditions, making them a cost-effective and long-lasting solution.
Moisture and Mold Resistance
Polymer insulation materials are known for their excellent moisture resistance, which helps prevent mold growth. This is particularly important in regions with high humidity, as it contributes to maintaining a healthy indoor environment.
Having mold-resistant insulation materials installed in the building ensures better air quality, preventing possible health issues related to mold exposure. Besides, polymer insulating materials are known to be resistant to outdoor elements that can lead to material degradation, ensuring a long service life.
Temperature Comfort and Air Leakage Control
Another advantage of polymer insulation is its ability to maintain a comfortable temperature in the building and effectively control air leakage. By creating an airtight seal, polymer insulation prevents drafts and greatly improves overall energy efficiency.
This ultimately leads to a more comfortable living space, allowing homeowners to enjoy better temperature regulation and improved indoor air quality. Moreover, due to its affordability and versatility, polymer insulation can be a cost-effective choice for homeowners seeking to improve energy efficiency and comfort in their homes.
In conclusion, polymer insulation materials offer a wide range of benefits to homeowners. Their lightweight and durable nature, moisture and mold resistance, and excellent temperature comfort and air leakage control make them an energy-efficient, comfortable, and affordable option for both residential and commercial applications.
Life-Cycle Analysis of Polymer Insulation
When considering the environmental impact of construction materials, it is essential to assess their life-cycle analysis. This analysis evaluates the environmental effects associated with a product’s entire lifespan, from raw material extraction to disposal or recycling.
In the case of polymer insulation, conducting a life-cycle analysis helps determine its overall sustainability.
Polymer insulation generally has a favorable life-cycle profile due to several factors. Firstly, polymers are lightweight materials that require less energy for transportation and installation compared to traditional alternatives like concrete or metal.
This reduces greenhouse gas emissions during transportation and lowers fuel consumption.
Polymer insulation often contains recycled content derived from post-consumer waste or industrial byproducts. By incorporating recycled materials into production processes instead of relying solely on virgin resources, manufacturers can reduce energy consumption and minimize waste generation.
Furthermore, many types of polymer insulation have excellent durability properties that contribute positively to their life cycle assessment (LCA). Long-lasting products result in reduced replacement needs over time and lower resource consumption as well as decreased waste generation throughout their service lives.
Lastly but importantly for LCA considerations is end-of-life management options for polymer insulations such as recycling possibilities which can further enhance its sustainability credentials by reducing landfilling rates while recovering valuable resources at the same time.
Polymer Insulation for High-Temperature Applications
Traditional insulation materials such as fiberglass or mineral wool may not be suitable for these extreme conditions, making polymer insulation a preferred choice.
One type of polymer commonly used in high-temperature applications is polyimide foam. This material exhibits excellent thermal stability and can withstand temperatures up to 300°C (572°F).
It has low thermal conductivity, which means it effectively reduces heat transfer and helps maintain a stable temperature within the insulated area.
Another option for high-temperature insulation is silicone-based polymers. These polymers have exceptional resistance to heat and can endure temperatures ranging from -60°C (-76°F) up to 230°C (446°F).
They are often used in industrial settings where machinery generates significant amounts of heat.
Polymer-based ceramic composites are also gaining popularity as an alternative for high-temperature insulation. These composites combine the lightweight properties of polymers with the superior thermal resistance of ceramics, offering enhanced performance at elevated temperatures.
When selecting polymer insulation for high-temperature applications, it’s crucial to consider factors such as temperature range requirements, durability under prolonged exposure to heat, fire resistance capabilities, and compatibility with other construction materials or systems present in the application area.
Fire Resistance of Polymer Insulation
Unlike traditional insulation materials, such as foam or fiberglass, polymer-based insulations are inherently flame retardant. This means that they have a high resistance to ignition and do not contribute significantly to the spread of flames.
The fire-resistant nature of polymer insulation is attributed to its chemical composition and structure. Polymers used in these insulations are often formulated with additives that enhance their ability to withstand heat and flames.
These additives work by releasing gases when exposed to high temperatures, creating a protective barrier between the flame source and the surrounding material.
Some polymer insulations undergo intumescent reactions when exposed to fire or extreme heat conditions. Intumescence refers to an expansion process where the material swells up upon heating, forming a thick char layer on its surface.
This char layer acts as an effective thermal barrier by slowing down heat transfer through conduction.
It is important for builders and homeowners alike to consider using fire-resistant polymer insulation in their construction projects for enhanced safety measures against potential fires.
Cost Efficiency of Polymer Insulation
Polymer insulation stands out in this regard due to its affordability and long-term savings. Compared to traditional insulating materials like fiberglass or mineral wool, polymer insulation offers a more cost-effective solution.
One of the reasons for the cost efficiency of polymer insulation is its lightweight nature. This makes transportation and installation easier and less expensive compared to heavier alternatives.
Polymer insulations are often available in pre-cut panels or rolls that can be easily handled by one person, reducing labor costs during installation.
Another aspect contributing to the overall cost effectiveness of polymer insulation is its excellent thermal performance. These materials have low thermal conductivity which means they effectively reduce heat transfer through walls, roofs, or floors – resulting in lower energy consumption for heating or cooling purposes throughout the year.
Furthermore, unlike some other types of insulating materials that may degrade over time due to moisture absorption or settling issues leading them losing their effectiveness over time; high-quality polymers are known for their durability and resistance against moisture damage ensuring long-lasting performance without compromising on energy efficiency.
Innovations and Future Trends in Polymer Insulation
1. Nanotechnology: Researchers are exploring the use of nanotechnology to enhance the performance of polymer insulation materials. By incorporating nanoparticles into polymers, properties such as thermal conductivity, fire resistance, and mechanical strength can be significantly improved.
2. Sustainable Materials: With a growing focus on sustainability in construction, there is an increasing demand for eco-friendly insulation solutions.
Manufacturers are developing polymer insulations made from recycled or bio-based materials that offer comparable performance to traditional options while reducing environmental impact.
3. Smart Insulation Systems: The integration of smart technologies into polymer insulation systems is gaining traction.
These systems utilize sensors and actuators embedded within the material to monitor temperature changes, adjust thermal properties accordingly, and optimize energy efficiency in buildings.
4. Aerogel-Based Insulation: Aerogels are lightweight materials with exceptional insulating properties due to their high porosity and low density structure.
Ongoing research aims at incorporating aerogels into polymers for enhanced thermal insulation capabilities without compromising structural integrity.
5. Polymer Composites: Combining different types of polymers or blending them with other reinforcing fibers like carbon fiber or glass fiber can result in composite materials that exhibit superior mechanical strength while maintaining good thermal insulation characteristics.
6. Advanced Manufacturing Techniques: Additive manufacturing techniques such as 3D printing enable precise control over material composition and structure during fabrication processes for customized polymer insulations tailored specifically for each application’s requirements.
FAQ
Which polymer is very good insulator?
The polymer known as XLPE, an ethylene-based compound, is a superb insulator for power and telecommunications wires and cables.
What is polymer insulation?
Polymer insulation refers to a type of insulator utilized in both transmission and distribution power lines as well as substations, immensely beneficial for their mechanical resilience to shocks due to the inherent flexibility and behavior of polymeric materials.
What is the other name of polymer insulator?
The other name for a polymer insulator is a composite insulator.
Are polymers good insulators?
Yes, polymers are effective insulators due to their long, chain-like molecular structure enabling them to resist the flow of both heat and electricity.
What are the common types of polymers used in construction insulation?
The common types of polymers used in construction insulation include Polyurethane (PU), Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polystyrene, and Polyethylene.
How does the structure of polymers contribute to their insulating properties?
The structure of polymers contributes to their insulating properties by having long chains of repeating units with weak intermolecular forces, reducing their ability to conduct heat or electricity.
What are the environmental impacts of using polymer-based insulation in construction?
The environmental impacts of using polymer-based insulation in construction include potential pollution during manufacturing and disposal, but these are mitigated by increased energy efficiency and durability of buildings, leading to a net lower carbon footprint.
Recap




