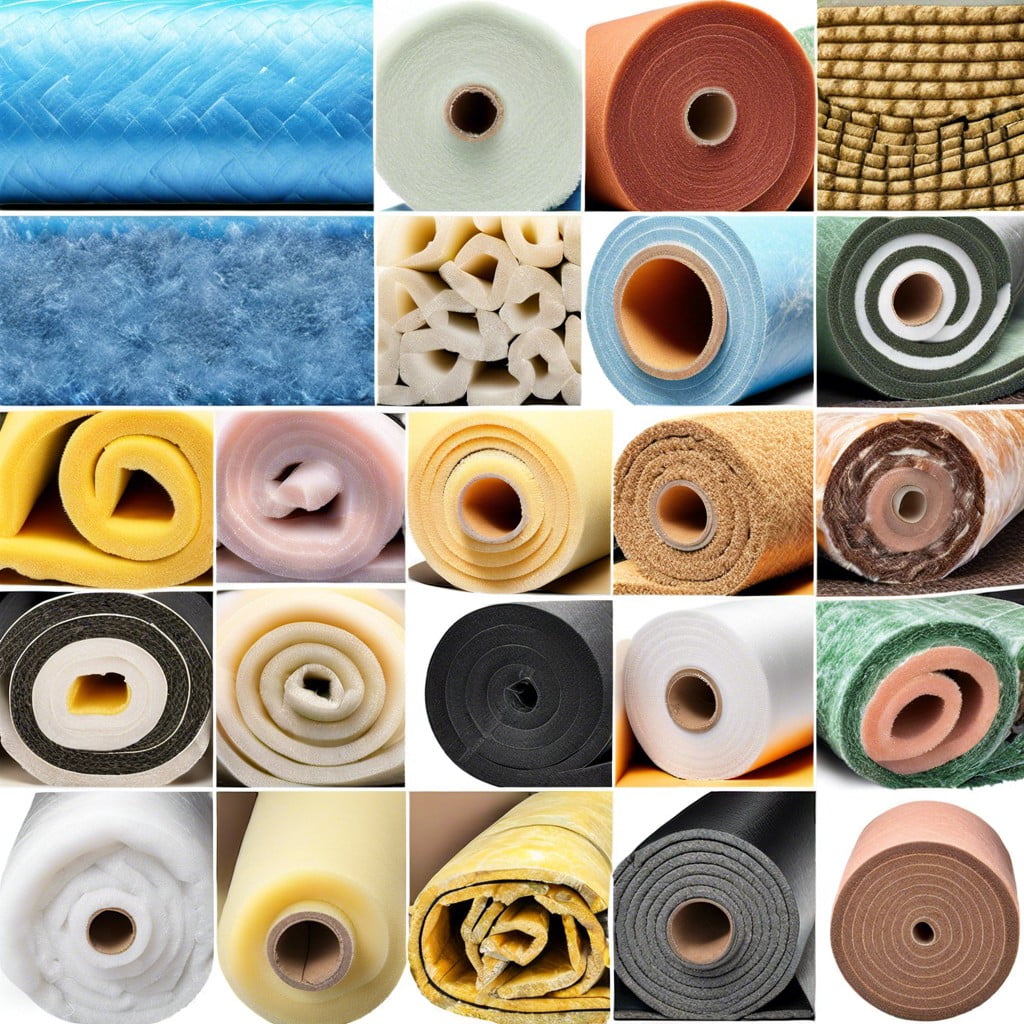
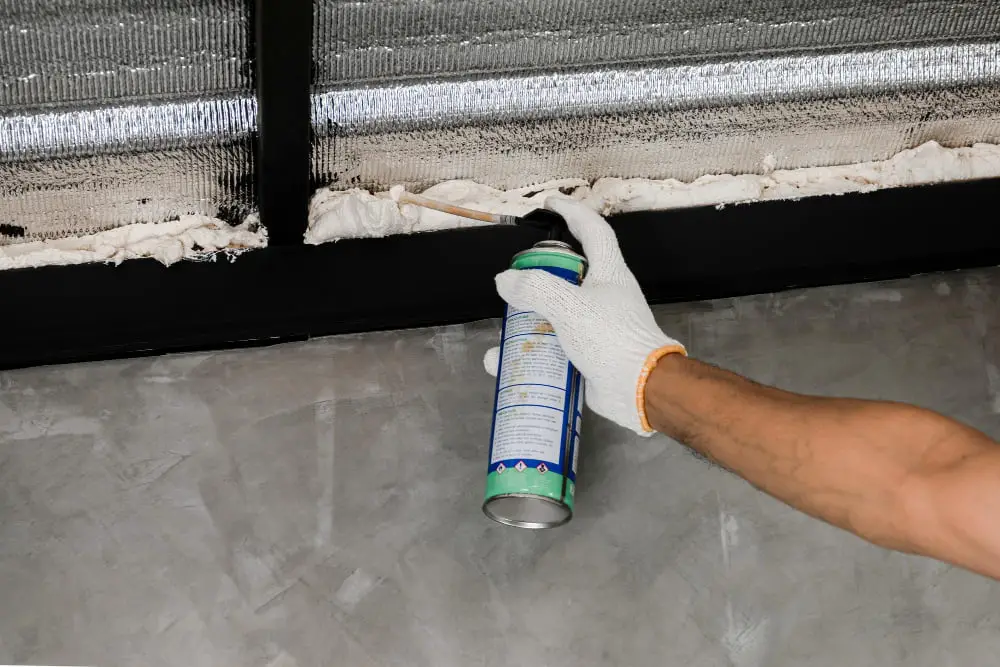
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore the benefits and applications of polymer foam insulation – a lightweight insulating material that can revolutionize your next construction project.
Polymer foam is an incredibly lightweight insulating material with many benefits.
In this blog post, we’ll explore everything you need to know about polymer foam insulation – from what it is and how it works to its advantages and disadvantages compared to other types of insulations.
By the end of this comprehensive guide, you’ll be equipped with all the knowledge you need to make an informed decision when choosing an insulating material for your next project or home renovation.
So let’s get started!
Introduction to Polymer Foam Insulation
Polymer foam insulation is a type of lightweight insulating material that has been gaining popularity in recent years. It’s made from a polymer, which is essentially a synthetic material that can be molded into various shapes and forms.
The foam itself is created by mixing the polymer with other chemicals to create an expanding agent, which causes it to expand and harden into its final form.
One of the main advantages of polymer foam insulation over traditional materials like fiberglass or cellulose is its ability to fill even the smallest gaps and crevices in walls, ceilings, and floors. This means that it provides better overall coverage than other types of insulation while also reducing air leakage – one of the biggest culprits for energy loss in homes.
Polymer foam insulation comes in two main types: open-cell and closed-cell. Open-cell foams are softer and more flexible than their closed-cell counterparts but have lower R-values (a measure used to determine thermal resistance).
Closed-cell foams are denser with higher R-values but tend to be more expensive.
If you’re looking for an effective way to insulate your home or building without adding extra weight or bulkiness, then polymer foam insulation may be worth considering as an option!
Types of Polymer Foams

These are the further types of polymer foams:
- Expanded Polystyrene (EPS) Foam: This type of foam is made from polystyrene beads that are expanded and fused together to create a rigid board or block.
- Extruded Polystyrene (XPS) Foam: XPS foam is similar to EPS but has a more uniform structure due to the extrusion process used during manufacturing.
- Polyurethane (PU) Foam: PU foam is created by mixing two chemicals together which react and expand into a solid mass with excellent insulating properties.
- Polyisocyanurate (PIR) Foam: PIR foam is similar to PU but has improved fire resistance due to the addition of flame retardants during production.
Each type of polymer foam insulation has its own unique characteristics and advantages depending on your specific needs for your project or home renovation.
If you’re looking for an affordable option with good thermal performance, EPS may be the way forward; if you need something stronger than EPS then XPS could be what you need; if fire safety concerns are paramount then PIR would make sense while polyurethane offers high R-value per inch making it ideal where space constraints exist.
Understanding each type’s strengths can help in selecting one that best suits your requirements when considering using Polymer Foams Insulation in construction projects or home renovations
Properties and Performance
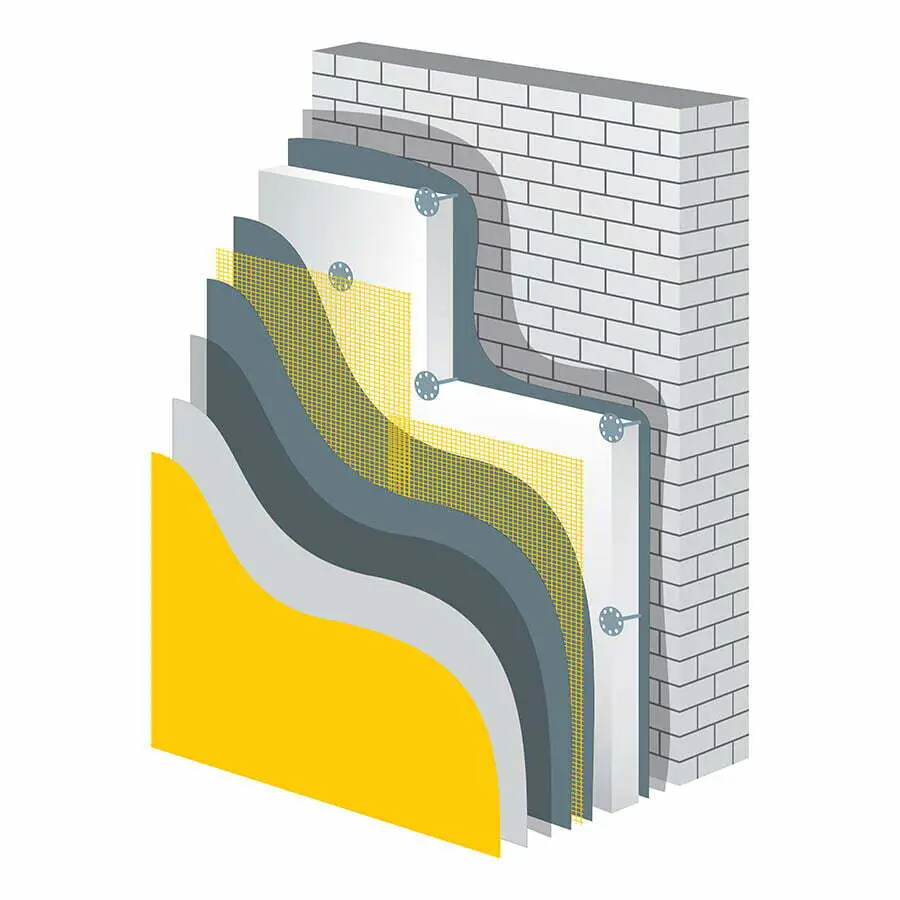
Polymer foam insulation is a lightweight and versatile insulating material that has gained popularity in recent years due to its unique properties. One of the most significant advantages of polymer foam insulation is its high thermal resistance, which means it can effectively reduce heat transfer between the inside and outside of your home.
This property makes it an excellent choice for homeowners looking to save on energy bills by reducing their heating and cooling costs.
Another advantage of polymer foam insulation is its ability to expand into small crevices, creating a tight seal that prevents air leaks. This feature not only improves energy efficiency but also helps keep out unwanted noise, dust, pollen, and other allergens from entering your home.
Polymer foam insulation also has good moisture resistance properties compared to other types of insulations like fiberglass or cellulose. It does not absorb water easily; hence it doesn’t promote mold growth or rotting over time.
In terms of performance, polymer foam insulation provides consistent R-values (a measure used for thermal resistance) throughout the life span without settling or compressing over time as some traditional materials do such as fiberglass batts.
Applications in Construction
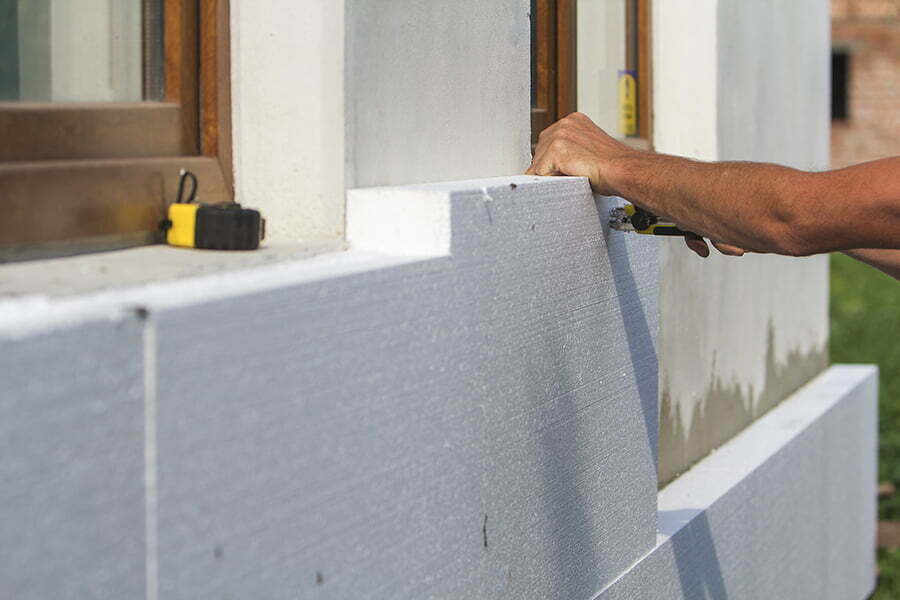

Polymer foam insulation has a wide range of applications in the construction industry. It can be used for insulating walls, roofs, floors, and even foundations. Its lightweight nature makes it easy to install and handle on job sites.
My friend who had recently installed polymer foam insulation in his home told me that he noticed an immediate difference in the temperature inside his house after installation. The material’s high R-value (a measure of thermal resistance) helps to keep heat from escaping during colder months while keeping cool air inside during warmer months.
In addition to its insulating properties, polymer foam insulation also acts as a sound barrier by reducing noise transmission between rooms or from outside sources such as traffic or airplanes passing overhead.
Another advantage is that it doesn’t settle over time like some other types of insulation materials do which means you won’t have gaps forming where heat can escape through your walls or roof.
Polymer foam insulation is an excellent choice for those looking for a lightweight yet effective way to improve their home’s energy efficiency and comfort levels all year round.
Installation Techniques
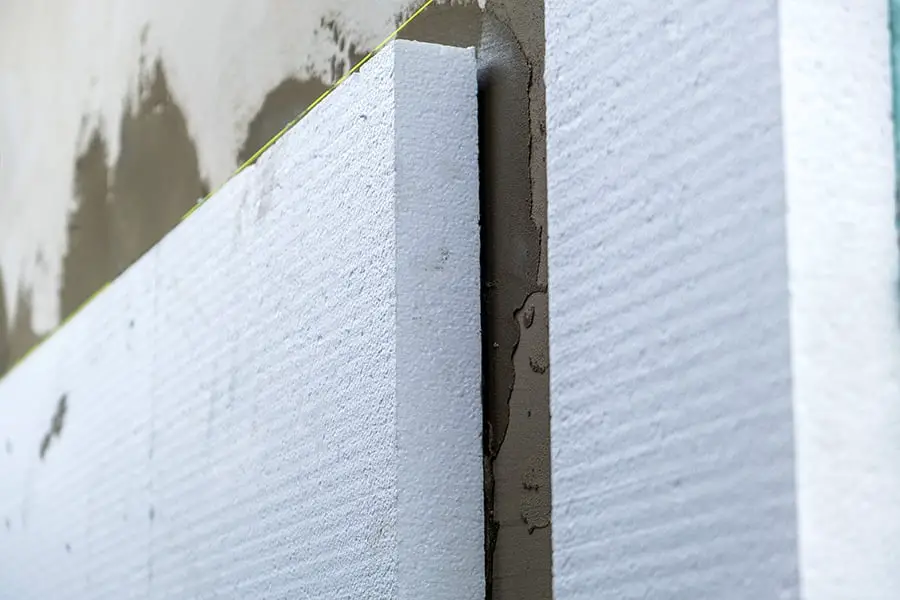

Now that we know what polymer foam insulation is and how it works, let’s talk about installation techniques. One of the biggest advantages of this type of insulation is its ease of installation.
Unlike traditional fiberglass batts or blown-in cellulose, which can be messy and time-consuming to install, polymer foam insulation can be applied quickly and efficiently.
There are two main methods for installing polymer foam insulation: spray application or injection into cavities. Spray application involves using a special machine to mix the liquid components on-site before spraying them onto surfaces such as walls or ceilings in a continuous layer.
Injection into cavities involves drilling holes into existing walls or other structures before injecting the material directly into those spaces.
Both methods have their pros and cons depending on your specific project needs. For example, spray application may be more suitable for larger areas with complex shapes while injection may work better for filling small gaps in existing structures.
Regardless of which method you choose, it’s important to hire an experienced professional who knows how to handle this type of material safely and effectively. Improper installation could lead to issues such as air leaks or moisture buildup over time – both things you definitely want to avoid when insulating your home!
If you’re looking for an easy-to-install lightweight insulating material that provides excellent thermal performance without adding extra weight load on your structure then Polymer Foam Insulation might just be what you need!
Environmental Impact

So what’s the verdict on polymer foam insulation? Well, while some types of foam insulation can have negative environmental impacts due to their manufacturing process and disposal methods, eco-friendly options are also available.
For example, some manufacturers use recycled materials in their production processes or offer recycling programs for used insulation products. Certain types of foams are made without harmful chemicals like CFCs or HCFCs which can contribute to ozone depletion.
It’s important when considering any insulating material – not just polymer foam -to do your research and choose an option with minimal environmental impact. By doing so you’ll not only be helping protect our planet but also ensuring a healthier living space for yourself and your loved ones!
Cost Analysis

Now that we’ve explored the benefits and drawbacks of polymer foam insulation, let’s take a closer look at its cost. As with any construction material, cost is an important factor to consider when choosing an insulating material for your project or home renovation.
Polymer foam insulation can be more expensive than traditional fiberglass batts or blown-in cellulose. However, it’s important to keep in mind that the initial investment may pay off in the long run due to its superior insulating properties and energy efficiency.
Some manufacturers offer different types of polymer foam insulation with varying costs depending on their R-value (a measure of thermal resistance). Higher R-values typically mean higher costs but also greater energy savings over time.
When considering the cost of polymer foam insulation compared to other materials, it’s essential to weigh all factors such as installation expenses and potential long-term savings on heating/cooling bills.
Ultimately, investing in high-quality lightweight insulating materials like polymer foams can lead not only to lower utility bills but also increased comfort levels within your home – something my friend experienced firsthand during those hot summer days!
Recap




