Exploring the factors that influence the cost of injection molding can provide valuable insights for those planning to invest in this method for polymer production.
The cost of injection molding, a popular method for manufacturing polymer components, is influenced by a variety of factors.
These include the type of material used, the complexity of the part design, the quantity of parts produced, and the specific requirements of the project.
Costs can range from a few thousand dollars for simple, small-scale projects to hundreds of thousands for large, intricate components.
This article will delve into each of these factors in detail, providing a comprehensive understanding of how injection molding costs are determined.
Key takeaways:
- Injection molding costs are influenced by material type, part complexity, quantity, and project requirements.
- Four main costs in injection molding: equipment, mold, material, labor.
- Equipment costs vary based on size, complexity, and productivity of machines.
- Mold costs depend on design complexity, material, size, and number of cavities.
- Material costs depend on grade, quantity, weight, and any special requirements.
Types of Costs in Injection Molding
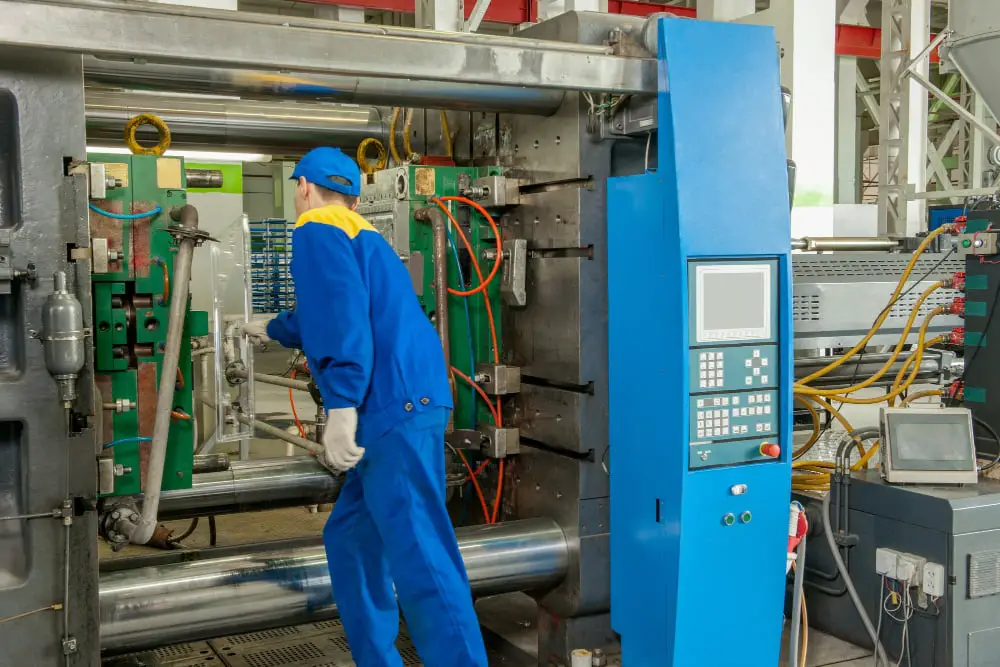

Four primary expenditures factor into injection molding: equipment, mold or tooling, material, and labor. The costs of equipment involve the purchase, operation, and maintenance of the machines used in the molding process. Equipment prices can vary considerably, with more advanced and automated machines costing higher.
Next is the mold cost, or the price paid for the custom-designed mold used to shape the polymer. Typically expensive due to precision engineering and high-quality materials required, the mold is reusable and vital in mass production scenarios.
Material cost refers to the price of the polymer used, which can differ greatly based on type and quality.
Lastly, labor cost is associated with personnel required to operate the machinery and oversee the production process. Other considerations under this cost type could include quality control, packaging, logistics, and administration.
Equipment Costs for Injection Molding
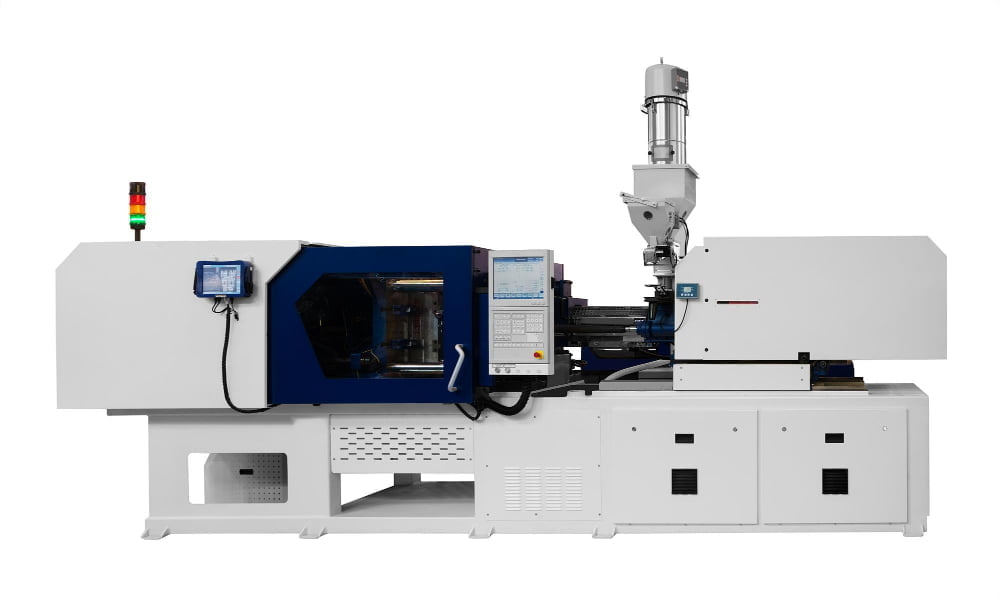

Injection molding machines are the cornerstone of any molding project. They come in a range of forms, each fit for different project sizes and types. The cost is significantly impacted by the size, complexity, and productivity of the machine.
- Desktop injection molding machines, the smallest and most affordable, are perfect for small, simple parts and low-volume production.
- Hydraulic machines, a bit larger and more powerful than desktop ones, have precise control of the molding process which makes them excellent for intricate parts.
- Electric machines, known for their energy efficiency and precision, come at a higher initial cost but can save money over time thanks to cost-effective operation.
- Lastly, hybrid models exist, blending the benefits of hydraulic and electric types can be a cost-effective compromise for suitable tasks.
Moreover, operational costs related to the machines, like electricity and maintenance, should also be taken into account. Finally, keep in mind that some projects might necessitate more than one machine, which further increases the starting cost.
Tooling or Mold Costs in Injection Molding
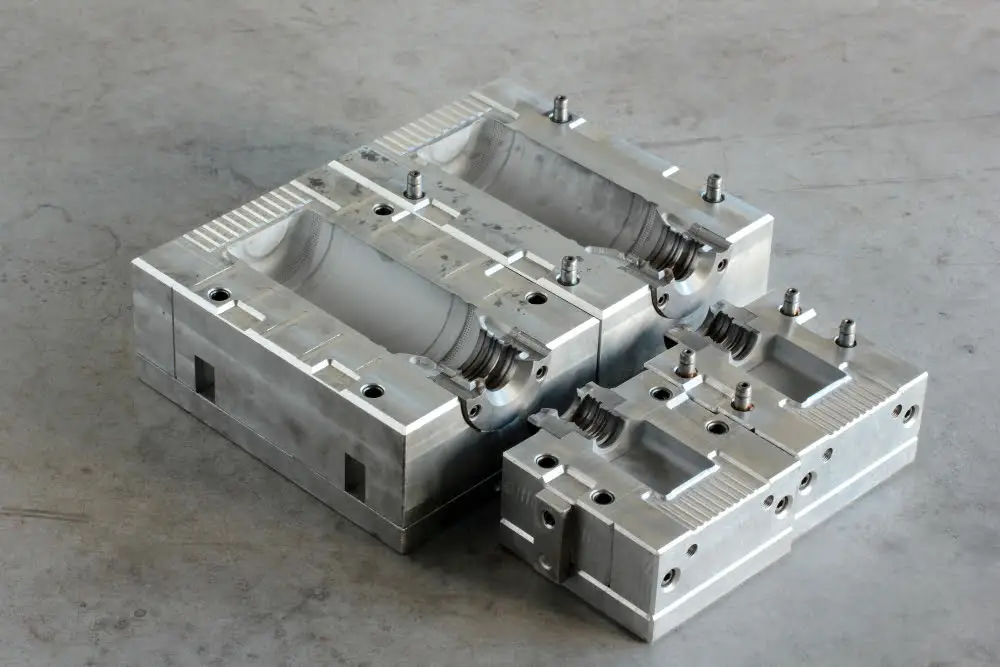
When it comes to the expense of tooling or molds in injection molding, several factors come into play.
First, the design complexity. Simply put, more complex designs require more intricate molds, subsequently increasing costs. In contrast, simpler and more uniform designs are easier to create and can lower costs.
Another important factor is the material used. Tooling materials like aluminum are cheaper but less durable, making them optimal for prototypes or smaller runs. Steel, on the other hand, can withstand numerous uses but at a higher price point.
Then there is mold size. Larger molds tend to cost more not only due to the increased material usage, but also because of the longer manufacturing time and effort.
Reflect on the number of cavities in the mold. A greater number of cavities increases the mold cost; however, it allows the production of more pieces per cycle, thereby improving the efficiency and balance of the overall cost.
Custom features for specific parts, such as threads or undercuts, add further to the mold cost.
Finally, maintenance over the lifespan of the mold must be considered. Wear and tear can necessitate repairs or, in extreme cases, replacement of the mold.
To control these costs, consider simplifying the design if possible, choosing the most cost-effective mold material for your production size, and keeping the mold well-maintained to extend its lifespan.
Material Costs in Injection Molding
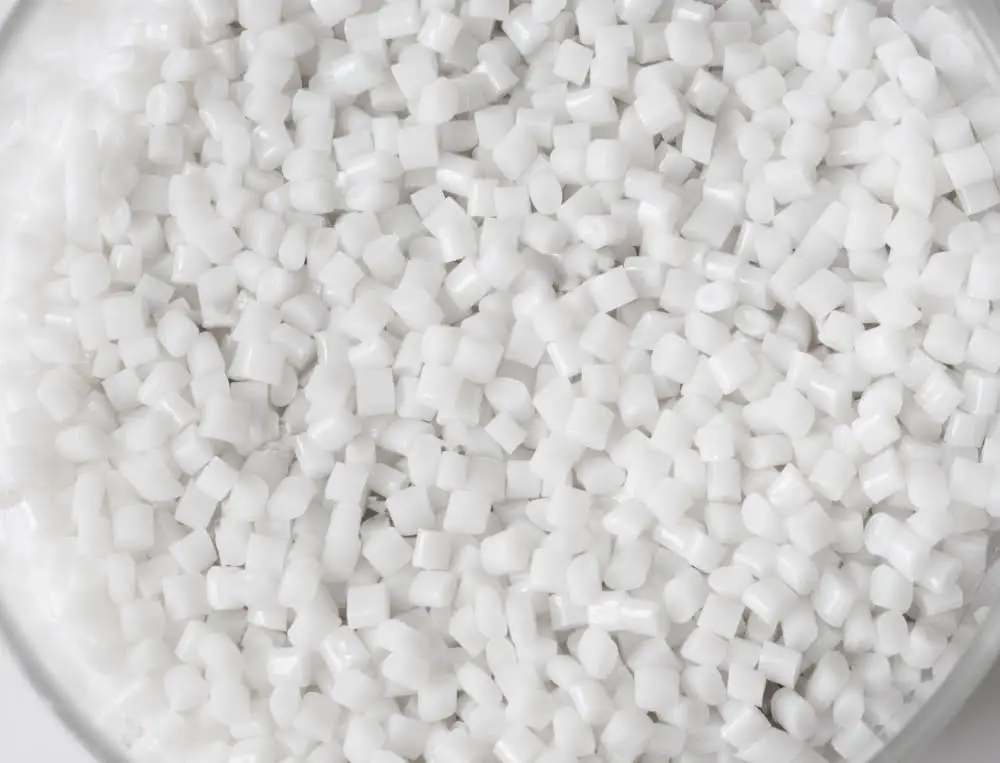

Choosing the right material largely dictates the cost-effectiveness and quality of a fabricated part. A myriad of factors influence the price.
The grade of the chosen polymer is crucial. Superior grades, like engineering-grade resins, are usually more expensive, though considerably more resilient.
The quantity of raw material also influences the cost. Greater production volumes tend to diminish the price per unit due to economies of scale.
The weight of the finished item plays a role. Bulkier parts require more raw material, hence incur a higher cost.
Also, any special requirements – UV resistance, flame-retardant, or other additives – will hike up the cost.
Remember, sourcing recycled plastics might reduce expenses, yet might compromise quality or properties of the final product. Such choice should be thoughtful, considering the application’s requirements.
Think about production rates and how the properties of the chosen material, such as cooling and setting times, might impact costs. More cost-friendly materials might require longer cycle times, an aspect not prominently noticeable until production.
Service or Labor Costs in Injection Molding

Service or labor costs encompass wages for skilled workers overseeing the injection molding process. This includes machine operators, quality control inspectors, and maintenance staff.
Machine Operators: Responsible for ensuring smooth operation of the injection molding machines, machine operators’ wages form a significant portion of labor costs.
Quality Control Inspectors: Crucial in maintaining the desired quality and consistency of the molded parts, the role of QC inspectors significantly contributes to the total cost.
Maintenance Staff: Regular preventive maintenance is essential for prolonging the life of the injection molding equipment and minimizing downtime. Hence, the cost of employing maintenance personnel is factored into the overall service cost.
Additionally, training costs for these staff members are also a part of the labor costs, especially in specialized molding techniques. It’s also worth noting that labor costs can greatly vary depending on the location and the complexity of the project.
One way to manage these costs is by optimizing the production process. Reducing cycle times, implementing real-time monitoring systems, and ongoing training can help improve efficiency and lower service or labor costs.
Variables Impacting Injection Molding Cost

Several factors can influence the overall cost of injection molding. One of the critical elements is the size and complexity of the part to be produced. Larger, more intricate parts require bigger, more complex molds, which adds to tooling costs. In contrast, simple and small parts can be produced using smaller, less expensive molds.
The type of plastic used also affects the cost. Certain plastics are more expensive or more challenging to work with, affecting both material costs and potentially labor costs as well.
Production volume is another crucial factor. Producing a large volume of parts can dilute the initial investment in equipment and molds, leading to a lower cost per part. Conversely, a small production run might have high setup costs, leading to a higher cost per part.
Operational efficiency is also vital. A more efficient production process, which produces fewer defective parts and maximizes the use of materials, can help lower costs.
Lastly, geographic location may impact price. Labor costs and the cost of space can vary depending on the location of the production facilities. So, choosing a manufacturer in a region with lower operating costs can substantially reduce the overall cost of manufacturing.
Strategies for Reducing Injection Molding Costs

When planning for cost reductions in injection molding, consider the following strategies:
Optimize Part Design: Simplifying design can reduce the complexity of the mold, leading to decreased tooling costs. Appropriate planning in this phase can prevent costly modifications later on.
Utilize Appropriate Materials: Selecting the right material can significantly alter the price. Certain resins have similar properties yet varying costs. Researching material prices and their compatibility with your project is vital.
Consider Multi-Cavity Molds: Although more expensive initially, multi-cavity molds provide economies of scale. This approach is especially cost-effective for more significant production runs.
Reduce Post Molding Operations: Each additional process contributes to the total cost. By optimizing the part design to reduce or eliminate secondary operations, you can save money.
Improve Process Control: A number of machine process parameters influence cost effectiveness. Training staff to monitor and understand these can lead to more efficient production and cost reduction.
By keeping these measures in mind, one can make informed decisions to mitigate the production costs associated with injection molding.
Comprehensive Overview of Injection Molding Cost Calculators

Injections molding cost calculators, available online, provide quick estimates adjusting for multiple factors, with the inputs ranging from the type of mold material to production volume.
A primary component to consider is the size and complexity of the part. Large or intricate forms can raise costs due to increased resource needs.
Plastic types determine not only production costs but also the mold’s durability. Some polymers, like ABS or polypropylene, are more affordable but less robust, while advanced materials like PEEK add to the cost but increase lifespan.
Another aspect is the production volume. Higher volumes can lower the per unit cost, as the initial costs are spread out over a larger quantity.
Tooling time represents how long it takes to prepare, maintain, and turn off the equipment and is factored into the total cost. Keep in mind, longer tooling times will increase costs.
Lastly, injection molding cost calculators adjust for regional variations, such as labor costs, utilities, and other overhead expenses. By selecting your geographic area, you can obtain a more accurate estimate.
Remember, these calculators provide initial estimates. For a precise quote, detailed specifications and direct communication with a manufacturer are essential.
Understanding Quotes for Injection Molding Services

When evaluating quotes for injection molding services, several key aspects should be taken into account.
The quote should clearly state the costs of raw materials, highlighting if they are included or not. Always verify the type of polymer used as the material price varies based on this.
Mold making cost should be specified in the quote. This includes design, prototyping, and manufacturing. Often, this is a significant portion of the budget.
The quote should detail the production costs. These costs encompass the actual molding of the piece, cycle time, testing, and quality control.
Packaging and shipping costs are often overlooked. Ensure the quote specifies whether these are included or will be charged separately. This aids in avoiding unwelcome surprises.
Understand any post-production services like assembly, decoration, or further machining, as these can significantly impact the final costs.
Lastly, note the number of parts being manufactured. In injection molding, a large quantity can drastically reduce the price per piece due to economies of scale.
To gain clarity, engage in a discussion with your service provider. Ask questions, request itemized cost breakdowns, and never hesitate to negotiate if there is room.
FAQ
How much does it cost to get an injection mold made?
The cost of an injection mold depends on the complexity and size, ranging from $1,000 for a simple single cavity mold, to over $80,000 for large or complex molds, with an average price around $12,000 for a typical mold of a relatively simple part.
How much does injection molding cost per hour?
The cost of injection molding per hour is $20 to $300+ per machine hour.
Why is injection molding so expensive?
Injection molding is expensive due to the complexity and labor-intensive nature of designing, creating, and assembling the molds, which require the work of highly trained specialists.
How much does injection molding cost per kg?
The cost of injection molding materials, commonly thermoplastics, typically ranges from $1 to $5 per kilogram, though the final price may vary due to other influencing factors.
What are the prominent cost factors in the injection molding process?
The prominent cost factors in the injection molding process include the cost of raw materials, energy consumption, labor expenses, and the initial costs of the molding machine and its maintenance over time.
How does the complexity of the part design impact the overall cost of injection molding?
The complexity of the part design directly impacts the overall cost of injection molding as more intricate designs necessitate advanced molds, increased production time, and higher material usage.
How does the material selection influence the cost of injection molding?
Material selection directly influences the cost of injection molding as the price, quantity required, and processing characteristics of the selected polymer can significantly affect the overall cost of the process.
Recap