In this article, we delve into the step-by-step process of pulling a vacuum on plastic for cable extrusion, ensuring high-quality and performance in your cables.
Pulling a vacuum on plastic for cable extrusion is a crucial step in the production process. It ensures the insulation layers fit snugly around the cable, providing superior protection and performance.
The process begins by heating the plastic until it reaches a pliable state. Next, a vacuum is applied, removing air and other gases, and effectively drawing the plastic tightly around the cable.
By following a specific set of steps, you can achieve a perfect vacuum pull every time. This article will guide you through these steps, ensuring that you understand the process thoroughly and can apply it effectively in your cable extrusion tasks.
Key takeaways:
- Vacuum system selection: Choose a system that maintains a constant vacuum level.
- Desired vacuum level: Mid-range vacuum helps in shaping and cooling plastic.
- Vacuum aids plastic degassing and removes gas bubbles for smooth surfaces.
- Vacuum system should be environmentally friendly and properly sized and placed.
- Precise material conveyance, screw design, and material grade selection are crucial.
Vacuum Requirements in Plastic Cable Extrusion
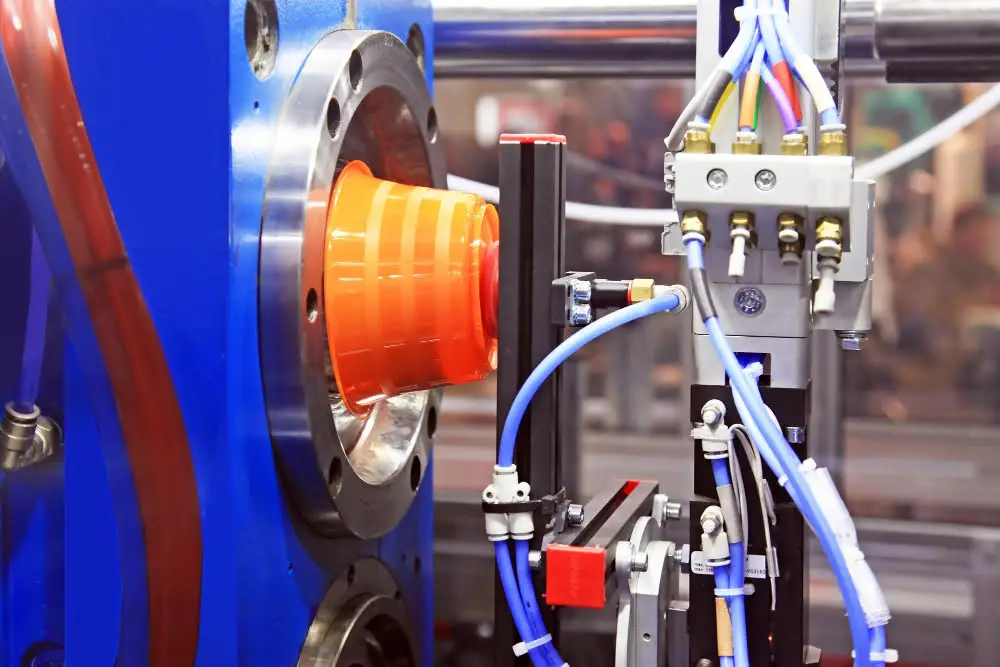
A vacuum system plays an integral role in plastic cable extrusion, capable of enhancing the throughput and quality of the final product. The presence of a vacuum assists in pulling the molten material through the extruder, improving the uniformity of density and shape.
Selection: Choose a system that maintains a constant vacuum level to ensure product consistency. It should handle varying process conditions and power consumption.
Vacuum Level: The desired vacuum level in cable extrusion typically ranges from 10 to 30 inHgV. This mid-range vacuum helps in shaping and cooling the extruded plastic.
Plastic Degassing: A vacuum helps in degassing the plastic. The removal of gas bubbles creates a smoother, higher-quality surface on finished cables.
Environmental Control: The vacuum system should not contaminate the workplace or environment. It should not release plastic vapor or gas into the atmosphere.
Size & Placement: Consider the physical size of the vacuum system. It should fit comfortably within your operational space and be located at the downstream end of the extruder.
The application of these key principles ensure the efficient utilisation of vacuum in cable extrusion, contributing to superior product quality.
Role of Plastic in Cable Extrusion
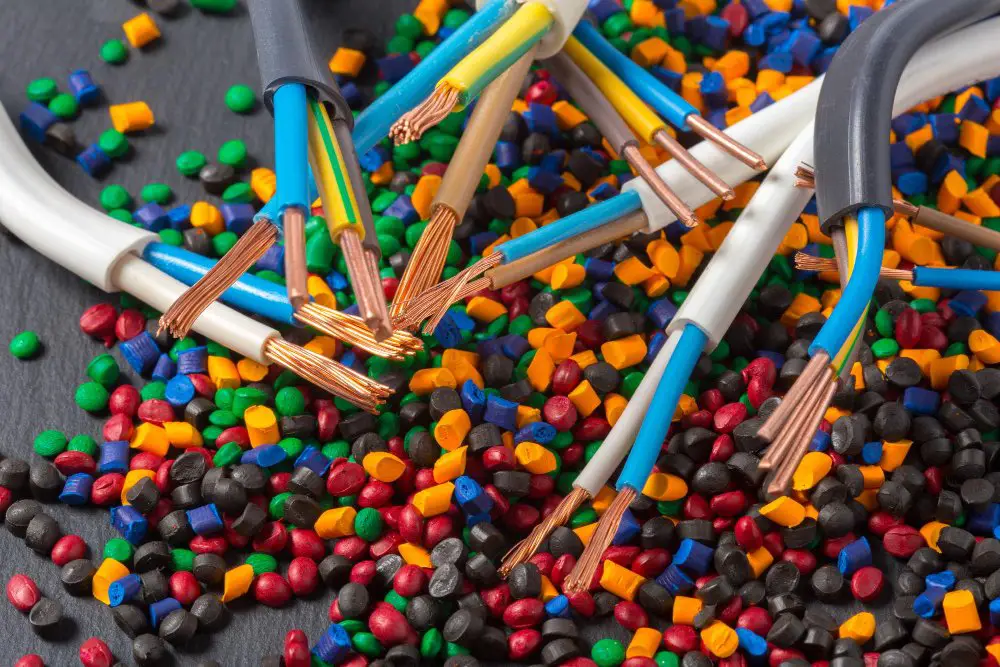

Polymers, specifically plastics, have become a foundational material in the cable extrusion process due to their exceptional insulating and protective properties.
Plastics create a barrier that safeguards the inner conductive wires from external environmental threats such as moisture, heat, mechanical stress, and the like. The PVC, Polyethylene, and Polypropylene, among others, are the most commonly used types, with each bringing their unique qualities to the table.
The plastic extrusion process involves melting the raw plastic material and shaping it to encapsulate the conductive parts of the cable. Careful control of temperature and pressure during this stage ensures an optimal plastic layer without imperfections, supporting a durable and high-quality cable product.
The plastic’s ability to endure the extrusion process, along with its variable physical properties, can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different cables. Whether it’s for enhancing flexibility, ensuring superior insulation, or adding flame-resistant traits, plastics play a dutiful role in shaping reliable and resilient cables.
Appropriate Material Conveyance for Cable Extrusion

When it comes to optimizing the cable extrusion process, material conveyance is a key consideration.
Firstly, precise control of material flow is vital to ensure even cable coating. This is usually achieved using a process-driven approach, often with a signal from a downstream monitor to adjust feed rates.
Second, in order to improve quality, some systems can incorporate devices that measure the speed and tension of the wire before it reaches the extrusion head. These controllers can then adjust the speed of the extruder and take-up to maintain consistent line pressure.
Third, selecting the optimal screw design for your extruder is a critical factor as it affects everything from material feeding to melting and mixing.
Lastly, material grade selection can significantly impact the viscosity of the plastic during extrusion, which influences the efficiency of the vacuum pull and the quality of the final cable.
These considerations all contribute towards a finely tuned cable extrusion process. Improvement in any of these areas can lead to increased productivity, superior product quality, and ultimately, higher customer satisfaction.
Selection of Suitable Vacuum Pump for Plastic Extrusion

Choosing the right vacuum pump is crucial in obtaining ideal conditions for plastic extrusion. Here are some crucial considerations:
Type of Vacuum Pump: Centrifugal and positive displacement pumps are the most common options. The chosen pump must be able to handle the volume of extruded material, and heat generated in the process without fail.
Capacity and Power: It’s essential to match the pump’s capacity with the volume of plastic to be extruded. Similarly, the pump’s motor should be powerful enough to maintain required pressure levels.
Heat Resistance: The extrusion process generates a significant amount of heat. Therefore, a pump with strong heat resistance capabilities will provide a longer operation lifespan.
Maintenance: Pumps that are easy to maintain and clean can save significant time and effort, improving overall efficiency.
Appropriate Sealing: A properly sealed pump ensures no air leakage, maintaining the correct vacuum level and improving the quality of the extruded cables.
By keeping these factors forefront, the selection of the correct vacuum pump can make a significant difference in the overall plastic cable extrusion process, optimizing efficiency, and improving product quality.
Heat Management in Cable Extrusion

Heat management plays a critical role throughout the cable extrusion process as improper temperature control can adversely affect the quality of the final product. Balancing the heat involves a two-fold approach:
- Consistent Temperature Monitoring: Implementing regular checks using heat sensors or infrared thermometers can ensure that the plastic is at the right temperature as it moves through the extruder. Too high or low temperatures can deform the final product or cause processing inefficiencies.
- Appropriate Cooling Systems: After the plastic passes through the extruder, prompt cooling is necessary to solidify and maintain the shape of the extruded cables. This step is often achieved through water coolants or air jets, carefully controlled to avoid sudden temperature drops which may create stresses in the material.
Additionally, extrusion speed must be harmonized with the heating and cooling stages to reduce the risk of overheating or under-cooling. This synchronization ensures a smooth, efficient manufacturing process that consecutively yields high-quality cables.
Role of Thermoforming in Cable Extrusion
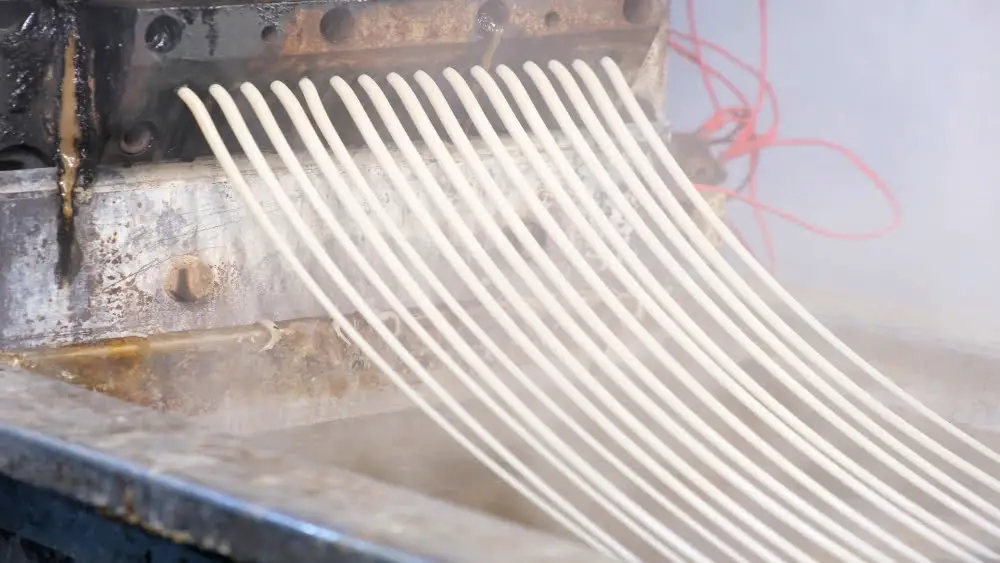

Thermoforming, essentially, is the process of heating a plastic material and forming it over a mold while it’s still in a pliable state, which is instrumental in the sphere of cable extrusion.
When we analyze the application of thermoforming in the context of cable extrusion, we need to remember these key points:
- Thermoforming involves heating the plastic until it reaches a soft state ideal for molding.
- The heat application must be carefully controlled to avoid any damage to the plastic and ensure uniformity in the final product. The temperature mostly depends on the specific type of plastic used.
- After the plastic has reached the desired temperature, it is shaped over or around a mold. This mold corresponds to the precise dimensions of the final cable casing.
- Cooling processes follow immediately to solidify the plastic into the desired shape.
- A key benefit of this process is that it allows for repeat production of uniformly sized and shaped cable sheaths.
In carrying out these steps, operators must ensure precise temperature control and timing to achieve consistent and quality outcomes. Recognizing the role of thermoforming plays an integral part in successfully carrying out plastic extrusion for cable manufacturing.
Wire Dewatering Processes in Vacuum Cable Extrusion

Wire dewatering, a vital step in vacuum cable extrusion, involves removing excess moisture from insulated wires post-extrusion. The process is essential in ensuring the final product’s high quality, optimizing its electrical properties, and prolonging its lifespan.
The main steps and concepts are:
- Application of Vacuum: A powerful vacuum pump applies significant suction, drawing out any excess water.
- Utility of High Temperature: Heat plays a crucial role, as the higher temperature speeds up the moisture evaporation.
- PVC Insulation Factor: For wires with polyvinyl chloride (PVC) insulation, dewatering ensures the removal of any trapped water within the wire.
- Importance of Timing: Timing is crucial. The process must not last too long to prevent insulation damage, or too short which might leave residual moisture.
- Fine-Tuning of Vacuum Level: Depending on the wire type and insulation, the vacuum level may need adjustments for optimal dewatering.
- Residual Moisture Monitoring: Regular checks are essential to assess if the desired level of dryness has been achieved.
By understanding and applying these important steps and concepts correctly, one can ensure efficient wire dewatering during the vacuum cable extrusion process.
Separation, Filtration, and Condensation Techniques in Cable Extrusion

During the extrusion of cables, separation, filtration, and condensation techniques play integral roles in ensuring a smooth, continuous, and efficient process. These vital steps are unavoidable due to the need for clean, dry, and appropriately cooled cables.
In the separation phase, trained specialists effectively distinguish distinct materials based on their unique properties. Also, impurities are swiftly removed from the mix, ensuring a high level of material purity for increased quality and longevity of the cables.
Next, during filtration, there’s elimination of micro-level impurities from the materials. This further enhances the quality of the cables produced by making sure that no contaminants make their way into the final product. This process also helps to reduce the need for maintenance, saving operators both time and resources in the long run.
The condensation process involves reducing the heat generated during the extrusion process. High temperatures are common in cable extrusion but have the potential to negatively impact the quality of the output. This makes proper condensation pivotal in stabilizing the temperature levels of the materials involved. Cooling channels coupled with fans serve as practical solutions to minimize the temperature to required levels. Auxiliary cooling systems can also be incorporated in larger setups to provide that extra cooling punch necessary for hectic operations.
As operators in the cable extrusion business, understanding these processes and efficiently executing them can lead to the construction of excellent quality cables. This, in turn, can bring about increased customer satisfaction, repeat business, and stellar industry reputation.
Addressing Challenges in Plastic Extrusion Granulation
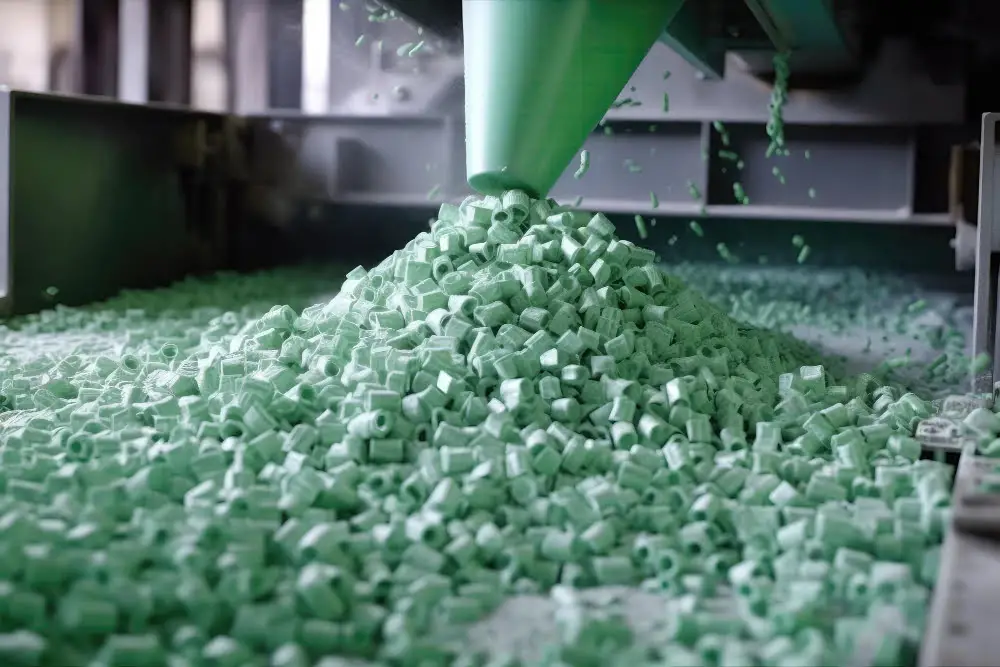

In mitigating challenges tied to plastic extrusion granulation, it’s vital to consider several aspects.
Firstly, the raw materials used must be of high quality. Any form of contamination can lead to inconsistent products which can be costly in the long run. Keeping the workspace clean and ensuring proper storage of the raw materials is key.
Secondly, monitoring the granulator temperature is of utmost importance. Overheating can cause the plastic to degrade, compromising the final product’s integrity. It’s advisable to incorporate cooling technologies within the granulator system.
Thirdly, the cutting chamber size must match the material being processed. If the volume of the plastic exceeds the chamber’s capacity, the granulator’s effectiveness can be severely hindered.
Additionally, regular maintenance is required. Even small malfunctions can escalate into larger issues if not addressed promptly. Regular inspections and replacement of worn-out parts ensures the longevity of the granulator.
Lastly, operational safety must be prioritised. Operators should be trained effectively on the correct use and potential hazards of the extrusion equipment. This minimises the risk of injury as well as potential equipment damage.
FAQ
What is the vacuum extrusion process?
The vacuum extrusion process is a technique used to consistently eliminate volatile substances during an extrusion operation.
How are plastic tubes extruded?
Plastic tubes are extruded by gradually melting the plastic material using mechanical energy and heaters, and then forcing the molten polymer into a die that shapes the plastic into a continuous tube, which then hardens upon cooling.
What is the process of plastic pellet extrusion?
The process of plastic pellet extrusion involves feeding plastic pellets from a hopper into a jacketed screw that, as it turns, transports, melts, and pressurizes the plastic, transitioning it from a solid state to a liquid and then reconstituting it as a finished component.
What materials are suitable for vacuum extrusion in cable production?
Thermoplastic materials such as polyvinyl chloride (PVC), polyethylene (PE), and polypropylene (PP) are suitable for vacuum extrusion in cable production.
How does extrusion temperature affect the quality of the plastic tubes?
The extrusion temperature directly affects the quality of plastic tubes, with too high temperatures leading to material degradation and too low temperatures resulting in improper melting and defective shaping.
What role do polymers play in enhancing the durability of extruded cables?
Polymers, such as polyethylene or PVC, enhance the durability of extruded cables by providing exceptional insulation, resistant durability to environmental and mechanical stresses, and reducing the cables’ susceptibility to damage.
Recap