Plastic extrusion products refer to various items manufactured using the plastic extrusion process, including tubing, piping, profiles for doors and windows, plastic films and sheeting.
Plastic extrusion products are a diverse group of items manufactured using a continuous process called plastic extrusion. This process involves melting raw plastic material, forcing it into a die to shape it, and then cooling it in that form.
The result is a wide range of products, from pipes and tubing to window frames and weather stripping. The versatility of this process allows for the creation of complex designs and the use of various types of plastic, making it a cornerstone of many industries, particularly construction.
As we delve further into this topic, we’ll explore the intricacies of the plastic extrusion process, the types of plastic used, and the myriad of products that result from this fascinating procedure.
Key takeaways:
- Plastic extrusion products are items manufactured using the plastic extrusion process.
- Plastic extrusion allows for the creation of complex designs and the use of various plastic types.
- Common extrusion products include pipes, tubing, profiles, films, and sheeting.
- Plastic extrusion offers benefits such as product uniformity, design flexibility, and the use of recycled materials.
- Different types of extruders, such as single-screw and twin-screw, are used in the plastic extrusion process.
Basics of Plastic Extrusion

The plastic extrusion process is a widely utilized manufacturing technique, involving the melting down of plastic material, which is then formed into a continuous profile. This method allows for the production of a variety of high-volume items such as pipe/tubing, weather-stripping, fencing, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheeting, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.
The primary stages of this process include feeding the raw plastic material into the extruder, melting and forming, cooling, and cutting or winding. Here, the raw plastic – often in the form of pellets or granules – is gravity-fed from a hopper into the barrel of the extruder. A rotating screw within the barrel conveys the plastic down its length, generating heat through friction and pressurizing the melt.
Once the plastic is thoroughly melted and mixed, it is forced through a die, which shapes it into the desired profile. The subsequent cooling can be achieved through air or water, or both. Depending on the specifications, the extruded product may also undergo additional processing to achieve specific properties or characteristics.
Implementing plastic extrusion can lead to significant benefits, such as uniformity of the final product, flexibility in design, and the use of recycled materials. It is essential, however, to understand that the efficiency and the quality of the outcome can be greatly influenced by factors such as the type of plastic, the design of the die, and the environment of the process.
Different Types of Plastic Extrusion Products

Plastic extrusion products vary widely depending on their application, shapes, and materials used. Products can essentially be created to fit a multitude of purposes.
Pipes and tubing often top the list with their varied uses in the construction industry, water systems, and heating ventilation and air conditioning systems. They can be created to resist certain temperatures and pressures making them versatile and reliable.
Next, you’ll find plastic profiles – these are continuous lengths with complex, uniform cross-sections. Used in items such as window frames, door frames, and weather stripping, plastic profiles are designed to withstand the elements.
Wire coating is another principal application. It involves sheathing or coating wires with a protective insulating layer. This is critical in electrical appliances, ensuring safety and function.
Sheet and film extrusion is widely used. This process produces plastic sheets or films that are too thick to blow. They are often used in the production of plastic bags and curtains, packaging films, and moisture barriers.
Lastly, we see the role of extruded products in different industries: consumer products like toys, automotive parts, and even medical instruments. This versatility highlights the ability of plastic extrusion to serve diverse needs across sectors.
Simply put, with the vast array of plastic extrusion products, there’s a high probability you’ve interacted with one today!
Screw Extrusion Process Explained

The screw extrusion process is a core aspect of plastic extrusion, closely involving the extruder, heating element, and resin pellets. Here’s a simple breakdown of the process:
- Resin pellets are loaded into the extruder. This is similar to loading a bench-mounted vise in relation to size and function.
- The resin pellets are then gravitationally driven into the barrel of the extruder where they are heated. This is akin to a pot on the stove, with the warmth coming from the heating elements that encircle the barrel.
- As the pellets move through the barrel atop a rotating screw, they transform into a liquid state due to heat and friction – imagine melting chocolate chips into a cohesive, liquid mass.
- The liquid plastic is then forced through a stationary screen pack and into the die to acquire the desired shape, which could range from flat sheets to complicated profiles. Consider it as a pastry bag squeezing out a fancy frosting design.
- Lastly, the shaped plastic is cooled and solidified as it moves along the production line. This is reminiscent of placing a warm, freshly baked cookie on a cooling rack.
Remember, the speed and temperature settings must be diligently monitored to ensure product consistency and quality.
Key Parts of a Single Screw Extruder
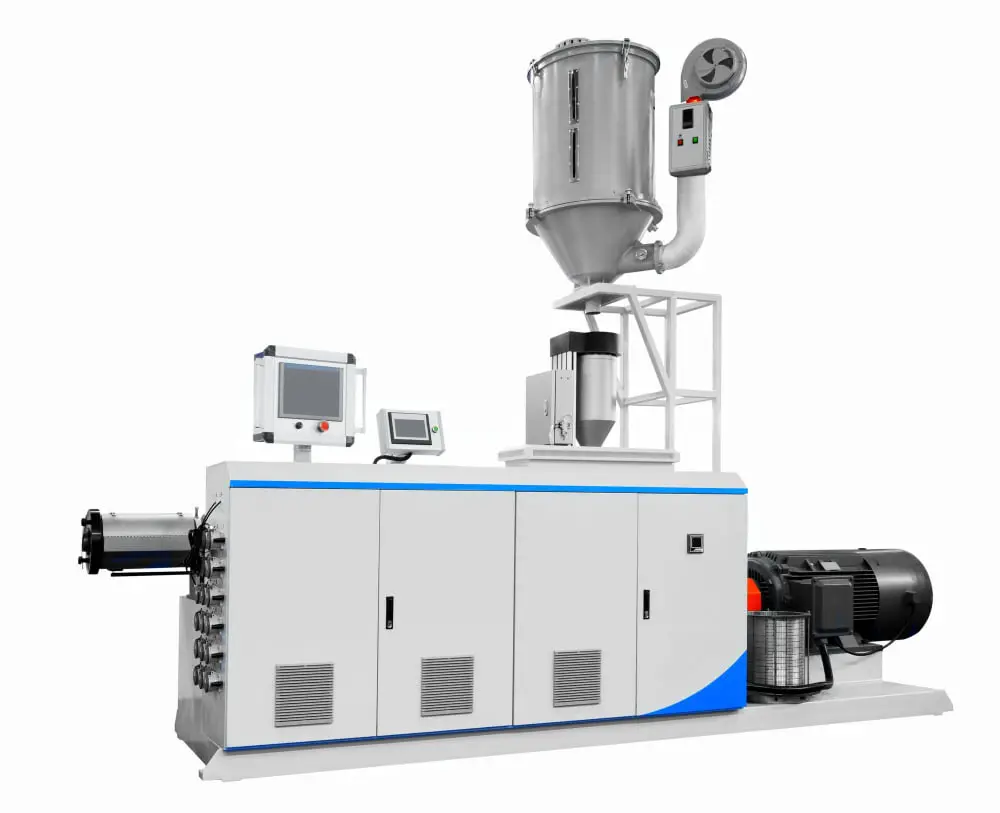

A typical single screw extruder is composed of several key elements that come together to facilitate the plastic extrusion process:
The Hopper: This component is significant as it’s the entry point for the raw plastic material. It directs the materials into the extruder.
The Barrel: The barrel forms the main body of the extruder. It’s the location where the plastic material is subjected to heat and pressure to achieve a malleable state.
The Screw: This part of the extruder plays an instrumental role. It’s a helical rod that rotates to help mix the plastic, apply heat, and feed the material through the barrel.
Heaters: These auxiliary components surround the barrel and aid in the heating process. They can be adjusted according to the type of plastic to optimize melting.
The Die: Positioned at the exit of the barrel, the die provides the final shape to the extruded plastic. The shape of the die opening determines the profile of the finished product.
The Cooling System: After the plastic is shaped, it needs to be cooled rapidly to retain its new form. A combination of air-cooling and water-cooling systems are typically used for this purpose.
Types of Extruders in Plastic Extrusion
Extruders play a crucial role in the transformation of raw polymers into a continuous profile. There are two primary types:
Single-screw extruders are the most common and versatile due to their ability to handle a wide variety of plastics at high speeds. They consist of a rotating screw within a stationary barrel which melts and moves the polymer towards the die.
Twin-screw extruders come in two configurations: parallel and conical. They employ two intermeshing screws, leading to improved mixing capabilities, better heat control, and increased output. However, they are more complex and costly.
Counter-rotating twin-screw extruders have screws rotating in opposite directions. Best used for PVC products, these extruders ensure consistent, high-quality outputs due to their superior homogenization, feeding, and venting capabilities.
Co-rotating twin-screw extruders have screws rotating in the same direction. They are ideal for compounding, mixing, and reactive extrusion due to their ability to ensure effective self-wiping action and more intense mixing.
The choice of extruder type depends on specific project requirements, including the type of polymer, the desired shape of the final product, and production speed.
Blow Film Extrusion: Details and Application
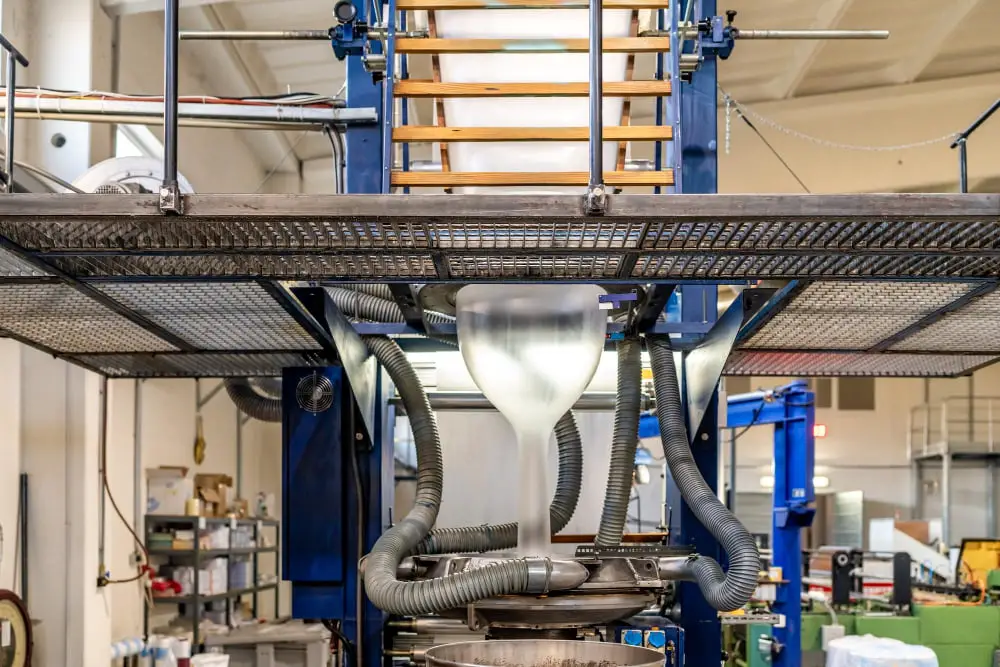

Blow film extrusion plays a crucial role in creating a variety of common plastic films. First, the plastic resins are earlier melted, and then extruded through an annular die, forming a tube of plastic or a “bubble”. The tube’s height gets controlled while simultaneously getting filled with air, creating the desired film width.
This extrusion method is often used to manufacture plastic bags and liners, as well as films for packaging perishables, in the food industry. The produced film can also be used as a protective barrier for more sensitive surfaces. Another application includes agricultural operations where it helps in the creation of greenhouses and mulch film.
The advantages of this method stem from its high production speed, excellent gauge control, and flexibility in film width. It’s also a cost-effective method as there is no need for a myriad of individual molds.
In the process of blow film extrusion, it’s critical to maintain consistent melt temperature to avoid variations in the thickness of the plastic. Also, proper control of cooling air is essential to set the film quickly and to prevent deformations.
To enhance specific mechanical properties of the finished product, the film can be oriented while still warm, either longitudinally, transversally, or in both directions, a process referred to as biaxial orientation.
Sheet Film Extrusion in Detail
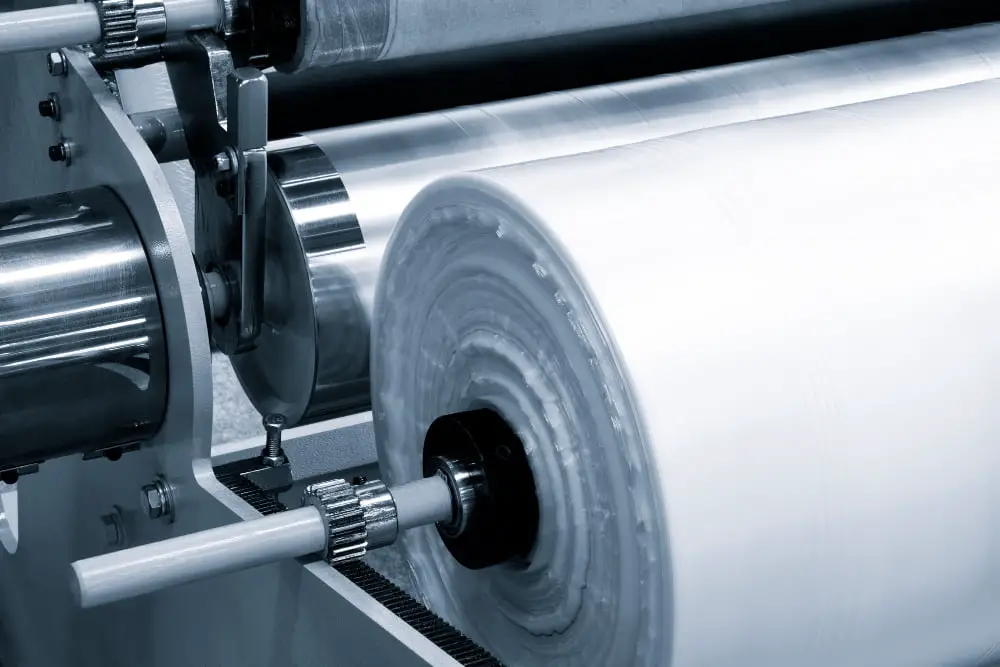

Sheet film extrusion involves the melting of raw plastic material, which is then passed through a set of shaping tools and cooled to create a thin, flat plastic sheet. This plastic sheet can be shaped and cut to a variety of lengths and widths, accommodating different industrial needs. The primary advantage to sheet film extrusion is the ability to create a continuous and uniform product.
Key Elements in the Process:
- Raw Material: The process begins with suitable plastic materials—either a single type or blend—to cater to specific requirements. Polyethylene and PVC are commonly used varieties.
- Heat and Pressure: Once prepared, the materials are heated to a specific temperature and forced through an extruder. The temperature and pressure applied must be managed carefully to ensure the resultant plastic sheet has homogeneity.
- Die: The extruded plastic is then passed through a sheet die, a shaping tool that determines the thickness and width of the sheet.
- Cooling and Setting: The hot plastic sheet exits from the die and immediately enters a cooling stage. It is then wound onto large rolls for distribution or further processing.
- Quality Control: Throughout, tight control systems must be in place to consistently monitor the thickness and width for any variations in the output.
Practical Applications:
- In construction, plastic sheets are cast-off to layer roofs, walls, and floors for protection and insulation.
- In the automotive industry, they’re moulded into various parts like dashboards and interiors.
- In agriculture, black plastic sheets prevent weed growth while also retaining moisture.
- The medical field makes wide use of plastic sheets in surgery kits, dental bibs, and protective covers.
Over Jacket Extrusion in Plastic Products: An Overview
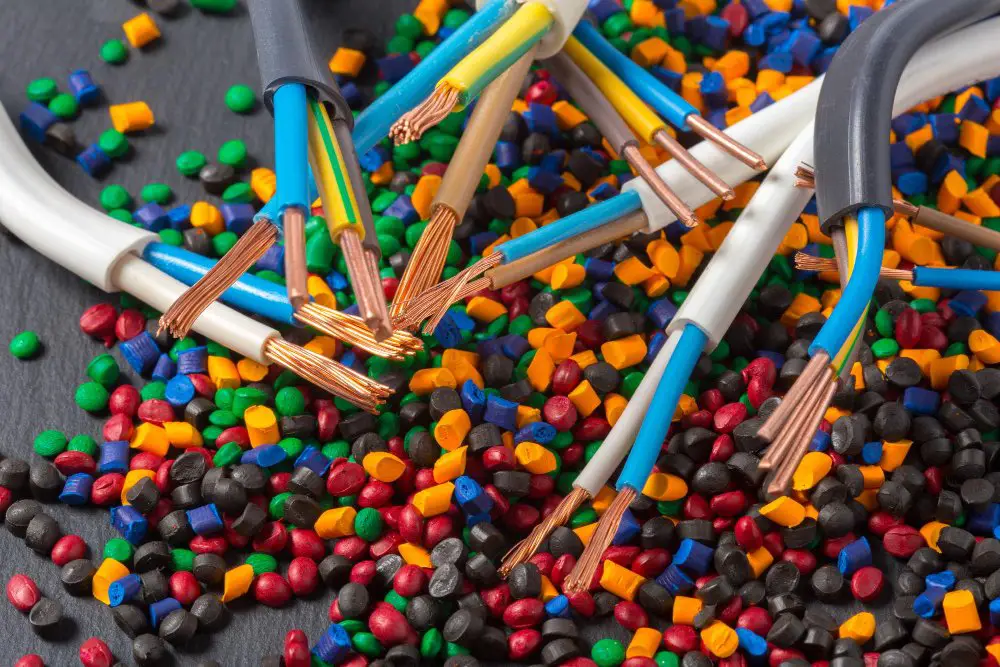

Over jacket extrusion serves an essential role in enhancing the functionality and efficiency of existing products in various industries. This specific method of manufacturing is predominantly utilized to create a protective layer for products such as wires and cables, ensuring their durability and longevity.
Key ideas related to over jacket extrusion include:
- Material selection: Polyvinyl chloride (PVC), thermoplastic elastomers (TPE), and polyethylene (PE) are the most used materials for over jacket extrusions, owing to their ability to offer excellent electrical insulation.
Application method: The conventional technique involves passing the core product through a die, then applying the plastic coating. It’s a continuous process, making it suitable for large-scale production.
Functionality: Over jacket extrusion provides physical protection to the product against environmental conditions like moisture, temperature, and pressure. It also offers electrical insulation in case of wires and cables.
Customization: The thickness, color, and texture of the jacket can be customized based on the requirement, further demonstrating the versatility of this process.
It’s important to note that executing over jacket extrusion requires specific machinery and skilled personnel to ensure precision and quality of the final product.
To oversee the process of over jacket extrusion for products:
- Identify the material requirements based on the desired characteristics of the jacketed product.
- Invest in or rent appropriate machinery to carry out the extrusion process.
- Train personnel in the use of extrusion machinery and in quality control procedures to ensure consistency in the end product.
- Ensure adherence to safety standards during operation to minimize potential hazards associated with the process.
Remember, proper planning and execution can greatly increase the efficiency and outcome of over jacket extrusion.
FAQ
What are some examples of products that are extruded?
Products extruded include pipes, tubing, wire insulation, thermoplastic coatings, sheeting, plastic films, window frames, deck railings, fencing, and weather stripping.
What household items are made by extrusion?
Household items made by extrusion include windshield wiper blades, squeegee blades, plastic rain gutters, automotive trim, and vinyl siding predominantly found in new home constructions.
What are extrusion Moulding product examples?
Extrusion moulding product examples encompass items like window glazing, machine guards, glass replacement materials, and packaging items including drinks bottles and blister packs for medications.
What are the key steps involved in the plastic extrusion process?
The plastic extrusion process mainly involves melting raw plastic material, forcing it into a die to create a shape, and then cooling it to create a continuous profile.
How does the plastic extrusion process contribute to sustainability in the construction industry?
The plastic extrusion process contributes to sustainability in the construction industry by recycling plastic waste into durable, high-performing, and potentially energy-efficient building materials, reducing waste and the sector’s carbon footprint.
What is the role of polymers in enhancing the quality of extruded construction products?
Polymers enhance the quality of extruded construction products by improving their strength, flexibility, durability, and resistance to environmental conditions.
Recap




