Discover the fascinating process of transforming medical waste into usable plastic extrusion, a sustainable solution that addresses both waste management and material scarcity in the construction industry.
The process of creating plastic extrusion from medical waste is an innovative solution to two pressing issues of our time: waste management and resource conservation. It involves transforming sanitized medical waste into reusable plastic through a series of steps including segregation, sterilization, shredding, and extrusion. This process not only reduces landfill waste but also provides a sustainable source of plastic for construction and other industries.
Dive into this article to learn more about each of these steps, the machinery involved, and the best practices to ensure a high-quality end product.
Key takeaways:
- Medical waste can be transformed into reusable plastic extrusion.
- Steps include segregation, sterilization, shredding, and extrusion.
- Sorting and categorizing medical waste is crucial for safe recycling.
- Thorough cleaning and preparation of plastics is essential for extrusion.
- Extrusion machines melt plastic and shape it into useful products.
Medical Waste As Raw Material for Plastic Extrusion
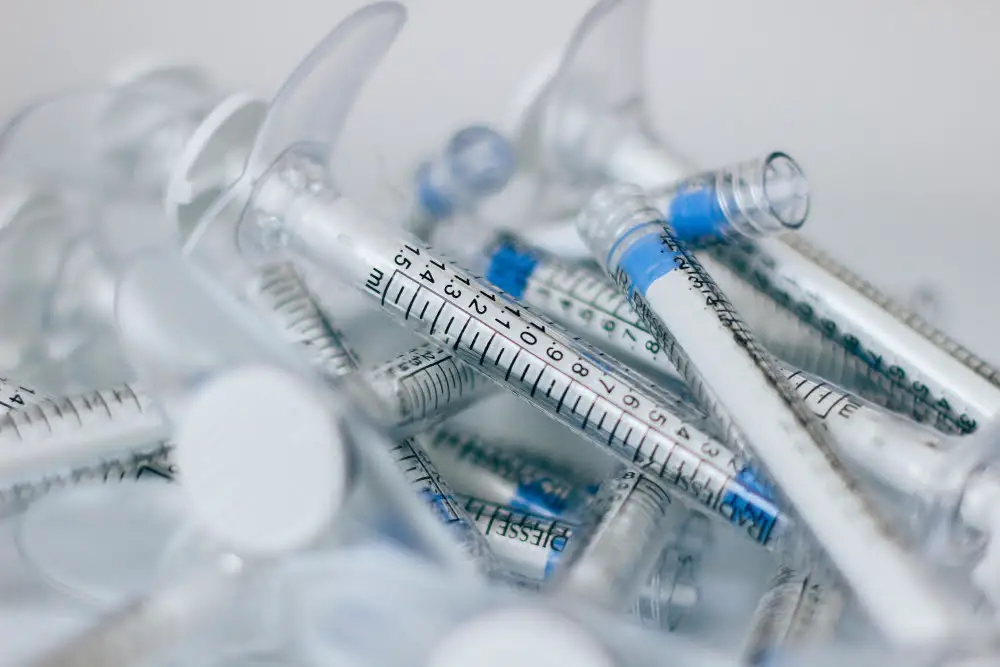
Medical waste, particularly those composed of plastics, serves as an invaluable raw material for plastic extrusion.
Often generated from hospitals, clinics, laboratories, and other healthcare facilities, this waste includes disposable items such as tubing, containers, bottles, and disposable gloves. Yet, instead of relegating these items to the landfill, they can be recycled and reintegrated into the production cycle.
Before this can happen, the waste should be collected and separated. It’s critical to distinguish between hazardous and non-hazardous types and ensure only safe, non-infectious waste is used for recycling.
The next step is the sterilization process. Any potential pathogenic substances are dealt with through autoclaving or incineration under meticulous conditions. And don’t forget, recycling professionals must adhere to meticulous rules to ensure safety and environmental standards are met.
Plastic materials suitable for extrusion can then be fermented or chemically processed to break down the complex chains into simpler forms. This preliminary stage significantly contributes to the efficiency of the plastic extrusion process.
After these steps are completed, the plastic waste becomes ready for the technical aspects of recycling, undergoing further cleaning, shredding and melting processes. These process turn them into useful plastic granulates for the extrusion. The recycling of medical waste into raw material for plastic extrusion is a beneficial method to reduce environmental pollution, save resources and produce useful products.
Sorting and Classifying Medical Waste

Medical waste comes in diverse forms, with varying properties and levels of hazardous elements. Efficient sorting and categorizing is vital for a safe and productive recovery process, particularly when the goal is to obtain plastic for extrusion.
Firstly, waste needs to be segregated into two main types – non-hazardous and hazardous. Non-hazardous waste includes items like office waste, sweeping, packaging, and food waste. The hazardous waste, the type of interest for plastic extrusion, contains plastics like gloves, syringes, tubes, bottles, and other disposable items.
In the next step, the non-plastic elements in the hazardous waste category must be isolated out. They might be metal parts of needles, rubber components, or residual bio-material.
Once the plastics are separated, further categorization based on the type of plastic is needed. Generally, medical waste includes polymers like Polyvinyl Chloride (PVC), Polypropylene (PP), and Polyethylene (PE). Proper identification of these plastics is crucial because each type of plastic has distinct extrusion parameters.
Lastly, a quality check has to be done to eliminate contaminated or degraded plastics. It’s of paramount importance to ensure that the plastics being passed through for extrusion are of acceptable quality.
Remember safety protocols should always be rigorously followed throughout the sorting and classifying process due to the nature of medical waste.
Extracting Plastics From Medical Waste

Healthcare facilities routinely generate substantial amounts of diverse waste types. A significant portion of this waste is plastic-based materials, notably single-use items such as syringes, gloves, catheters, and IV bags. Extracting plastic from this waste is a necessity not only for environmental conservation but also for effective waste management and resource recovery.
Clear distinction of non-hazardous waste: It’s crucial to only extract plastics from non-hazardous waste items, as certain medical wastes, like sharps or biological waste, could pose a risk.
Washing and sanitization: Any non-hazardous plastic waste should be thoroughly washed and sanitized, ensuring all biological contaminants are eradicated.
Shredding: The clean plastic items are then shredded into smaller pieces, enabling easier handling and processing.
Separation: Depending on the types of plastic used, there may be a need for separation. This typically includes separating by resin type, with common medical plastics including polypropylene, polyethylene, and PVC.
Decontamination: Further decontamination is carried out, often using advanced methods like pyrolysis, which also helps to reduce the volume of the waste.
Melt Filtering: The plastic waste is then often subjected to melt filtration to remove any remaining impurities before undergoing an extrusion process where it becomes a useful raw material for various applications.
Preparation of Extracted Plastics for Extrusion

Thorough cleaning of the extracted plastics eliminates contaminants like residual organic materials and enhances the quality of the final product. Here are the key steps in this process:
- Decontamination: Extracted plastics are put through an initial cleaning stage to remove any potential biohazard materials. Heat treatment is often applied to kill microorganisms and eliminate health risks.
- Washing: The decontaminated plastic is washed with a cleaning solution to remove any leftover dirt or grime.
- Drying: Post cleaning, the plastic is dried. This step is crucial as moisture can cause problems in the extrusion process.
- Grinding or Shredding: The dried plastic is then mechanically cut into smaller pieces, often called ‘regrind’, which are easier to manage in the extrusion process.
- Sieving: The regrind is then sieved to segregate by size and ensure uniformity, which promotes even heating and melting during extrusion.
- Preheating: The final step in the preparation process, preheating is done to remove any traces of final contaminants and moisture, ensuring the regrind is in the perfect condition for the extruder machine.
Remember, each step plays a pivotal role in preparing the plastic for extrusion and skipping even one can significantly affect the quality of the end product.
Working With Thermoplastic Resins in Extrusion

Once the plastics from medical waste are cleaned and prepared, they are transformed into a thermoplastic resin, a material that softens when heated and hardens when cooled. This malleability makes it an ideal candidate for the extrusion process.
Thermoplastic resins begin their journey in the form of pellets or granules. These tiny pieces are poured into the hopper of an extrusion machine. The hopper acts as the entry point for these pellets, directing them towards the extruder’s barrel.
Inside the barrel, the resin pellets encounter heat and mechanical energy provided by a rotating screw. As the screw turns, it creates shear and compressional stress, aiding the melting process and homogenizing the resin.
The molten plastic then progresses towards the die, which is designed to mold it into the desired shape. Careful control of temperature and pressure in the die is crucial to the success of this shaping stage.
Once the resin has passed through the die, it immediately enters the cooling and sizing stage to solidify into its final form. This rapid transition from the extreme heat of the die to the cooling unit is key to preserving the shape and integrity of the polymer product.
Smart selection of thermoplastic resins, careful management of temperatures, and precise control of pressures are your guides to maximizing the effectiveness of the extrusion process. In the case of medical waste-containing plastics, it’s no different, and using these variables ensures a high-quality end product.
Single Screw Extrusion Machine – How It Works
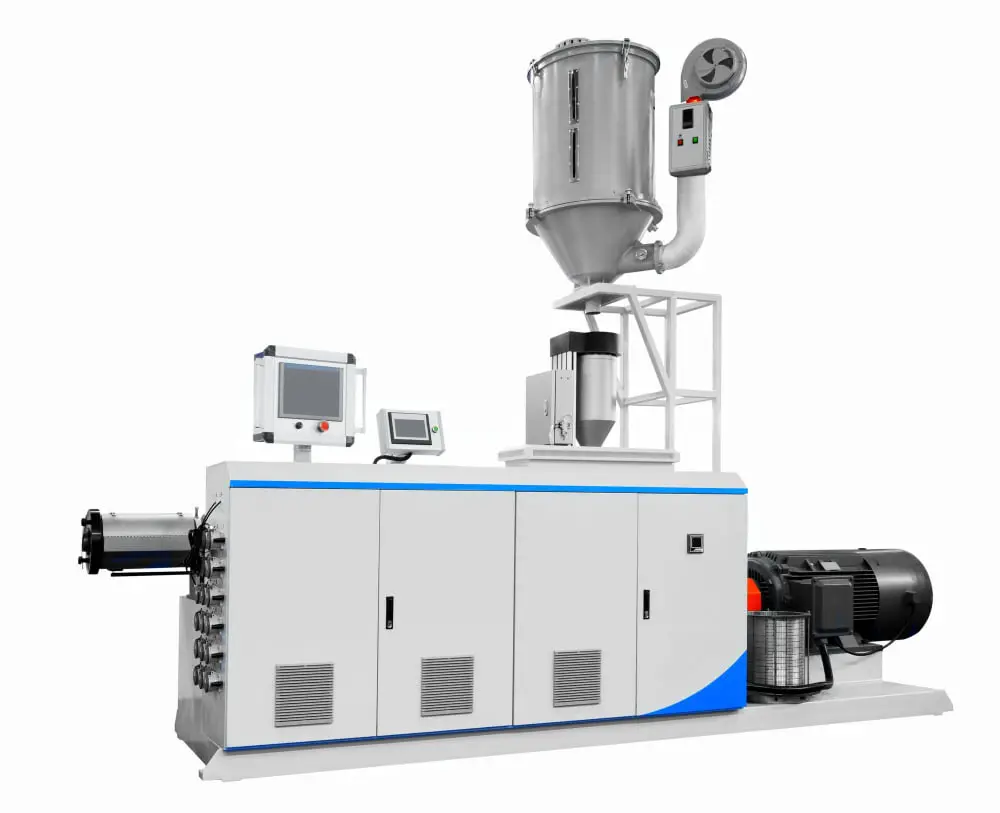

A single screw extrusion machine can be likened to a meat grinder, just for plastics. This machine takes pre-prepared pieces of plastic, which is fed into a hopper located at the top.
Here’s how the single screw extrusion machine powers this transformative process:
Firstly, the plastic bits drop into a long, rotating screw. Fueled by electricity, the screw spins and pushes the plastic along its length.
The plastic then comes into contact with a heater that melts it down into a gooey, molten state. The heat level is carefully controlled to prevent the plastic from breaking down chemically.
Next, the molten plastic moves down the channel, put under pressure by the mechanical work of the screw and the sidewalls. As the plastic moves forward, it gets more compacted and homogenous.
Given the channel narrows toward the end, the compacted plastic is forced through a specialized shape or die at the end of the machine as it leaves the screw.
Remember, the plastic takes the shape of the die – think cookie-cutter. This can range from pipes, sheets to other specialty shapes.
Once the plastic exits the die, it is cooled quickly to solidify it in its new shape. Often, water baths are used to remove heat rapidly.
Throughout the process, the operator can control the speed of the screw, offering control over how quickly the plastic is forced through the die. This impacts the final product’s dimensions.
Operating such an assembly requires understanding of plastic types, their melting points, and the rhythm of feeding in the material. Care, attention to detail, and safety are key.
Finally, routine maintenance like periodic cleaning of the screw and replacing worn-out parts is essential to ensure the optimum performance of the extrusion machine.
Investigating the Role of Extrusion Dies

Extrusion dies play a critical role in determining the final shape and dimensions of the extruded plastic. Essential parts of an extrusion line, these precision tools aid in forming the melted plastic into a continuously uniform profile.
Adaptable to different applications, the design of the die can be altered based on the product requirements.
For instance, simple flat dies, often used in sheet extrusion, feature a straight, relatively narrow flow channel leading to a wide, flat exit slot while pipe dies typically have an internal mandrel with a concentric, tubular exit.
The pressure applied through the die also has a direct impact on the quality of the finished product. Higher pressures often result in smoother, more defined shapes, but excessive pressure might lead to defects or distortion.
Die maintenance is key to delivering consistent results. Routine cleaning ensures residue build-up is minimized, ensuring a better quality of extruded plastic.
Temperature control is another crucial factor. Each resin type has a specific temperature range within which it performs optimally during extrusion. Maintaining the system within this temperature window can help prevent problems like sagging or lumpiness in the final product.
Lastly, adjusting the speed at which the extruded plastic is drawn out can influence the finished product’s thickness and strength. A slower draw speed tends to yield thicker, stronger pieces, while a faster draw can create thinner, more flexible plastics.
All these elements combine to determine how well the extrusion die performs its function. It’s not just about having a precision-made die; it’s about using it wisely and maintaining it properly. Learning to adjust and respond to these factors is a vital part of the plastic extrusion process.
Cooling and Sizing of Extruded Plastic
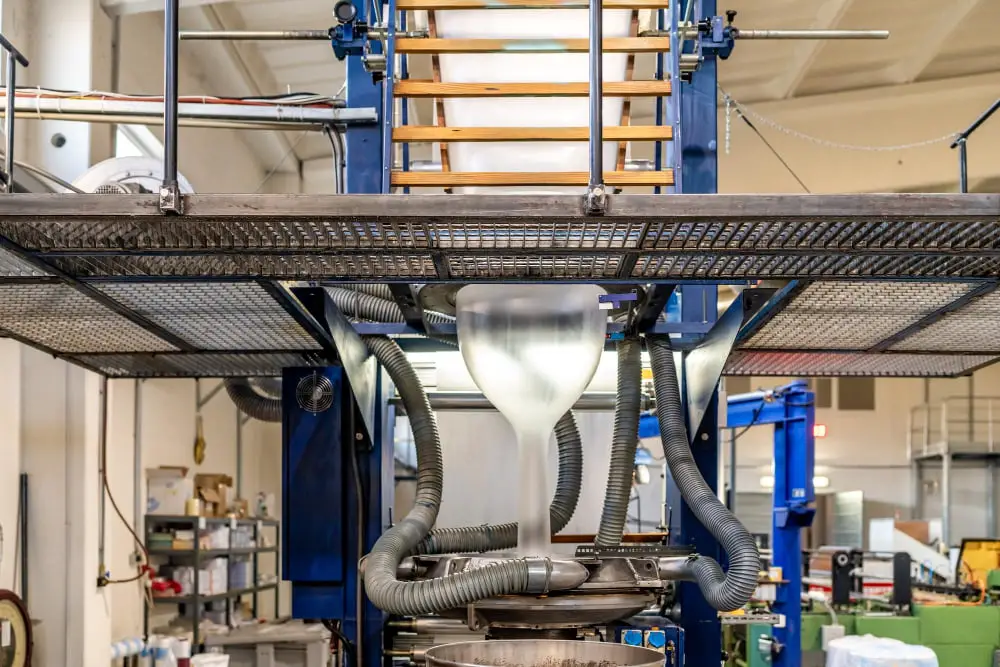

After passing through the extrusion die, the heated plastic needs to be cooled to hold its shape. For this process, a water bath is commonly used.
The sizing, on the other hand, can be done with the help of a sizing die, vacuum sizing, or cooling rings. In all methods, the aim is to bring the plastic to its final dimensions. A sizing die offers a precise size but works with certain types of plastics. Vacuum sizing pulls a vacuum on the plastic to enforce the shape, especially beneficial in tubing manufacturing. Cooling rings, often in use for blown film extrusion, use air to cool the plastic and control the bubble size.
In regards to the extrudate thickness, it can be adjusted by altering the take up speed: a faster speed decreases the thickness, while a slower speed increases it. By monitoring and adjusting these parameters, an almost endless variety of shapes and sizes can be achieved.
Turning Extruded Plastic Into End Products
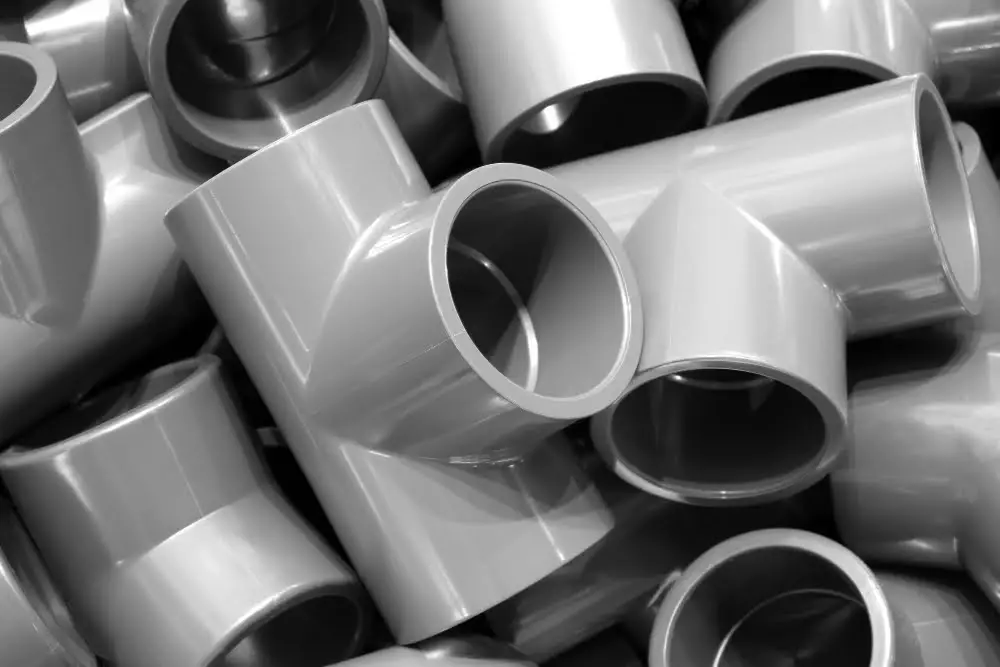

Once the cooling and sizing stages are completed, we can convert the plastic profiles obtained from extrusion into various useful end products. These transformations fall into two main categories: further processing and immediate use.
In the first category, the extruded plastic can undergo several treatments to meet different needs. These include:
- Cutting: The plastic profiles can be cut into specific lengths to suit their intended use. Commonly used cutting technologies range from simple mechanical cutters to advanced laser cutting systems.
- Surface finishing: Depending on the requirements of the final product, surface finishing procedures such as buffing, painting, or even embossing may be applied.
- Assembly: Sometimes, multiple cut pieces need to be assembled to form complex plastic products, such as housing units for medical devices.
Moving to the second category, treated plastic profiles might also have immediate applications. From plastic pipes for medical oxygen delivery to gloves and containers, extruded plastic sees a wide variety of uses in the healthcare field.
Bear in mind that converting extruded plastic from medical waste into end products requires careful consideration of health and safety standards, to ensure the end products pose no risk to users.
FAQ
How do you turn plastic waste into products?
Plastic waste can be transformed into new products through a process called mechanical recycling, where suitable plastics like PET and HDPE are cleaned, ground into powder, melted, and then converted into pellets that are reheated and reshaped.
What is the extrusion method of producing plastic?
The extrusion method of producing plastic is a high-volume manufacturing process that involves melting raw plastic and forming it into a continuous profile, resulting in various items like pipes, weatherstripping, fences, deck railings, window frames, plastic films and sheets, thermoplastic coatings, and wire insulation.
Can recycled plastic be extruded?
Yes, recycled plastic can be extruded using specific machines like the Extrusion Pro, which is capable of recycling up to 20 kg of plastic per hour and producing items such as beams and bricks.
What is the difference between injection molding and extrusion of plastic?
The key difference between injection molding and extrusion of plastic lies in their product outcome; injection molding is employed to produce three-dimensional shapes that vary rather than remaining constant along a straight line, whereas extrusion is utilized to create continuous two-dimensional, linear shapes.
What are the key steps involved in the recycling process of medical plastic waste?
The key steps involved in the recycling process of medical plastic waste include collection and segregation, cleaning and disinfection, shredding and granulating, and finally processing into new plastic products.
How does the quality of products made from recycled plastics compare with those made from virgin plastics?
While recycled plastics can yield high-quality products, they generally have slightly lower physical properties compared to those made from virgin plastics due to their previous heat histories and contamination.
How does the plastic extrusion process contribute to sustainable construction?
The plastic extrusion process contributes to sustainable construction by facilitating the manufacturing of durable, low-maintenance, and recyclable building materials from thermoplastics, minimizing energy consumption and waste production.
Recap




