The most common polymer is polyethylene. It is in various applications such as packaging, bottles, and plastic bags.
As a child, I was always fascinated by the colorful plastic toys that filled my toy box. From Barbie dolls to Lego blocks, each toy seemed to have its unique texture and durability.
As I grew older and began studying science, I learned that these toys were made from polymers – long chains of molecules that are used in everything from car parts to clothing.
But what exactly is a polymer, you may ask? Well, simply put, it’s a material made up of repeating units of smaller molecules called monomers. And while there are countless types of polymers out there, one stands out as the most common: polyethylene.
In this blog post, we’ll explore what makes polyethylene so ubiquitous in our daily lives and why it’s such an essential material in the construction industry. So sit back and get ready to learn about the wonders of this versatile polymer!
Key takeaways:
- Polyethylene is the most common polymer used in various applications.
- Polyethylene is versatile, durable, and has low cost.
- Polyethylene is commonly used in packaging, pipes, insulation, and vapor barriers.
- There are different types of polyethylene, including high-density, low-density, and linear low-density.
- Polyethylene has environmental challenges, but recycling technologies are advancing.
Introduction to Polymers
Polymers are everywhere around us, from the plastic bottles we use to the synthetic fibers in our clothes. They are an essential part of modern life and have revolutionized many industries, including construction.
But what exactly is a polymer?
As I mentioned earlier, polymers are materials made up of repeating units of smaller molecules called monomers. These monomers can be natural or synthetic and can vary in size and shape depending on the type of polymer being formed.
Polymers come in different forms such as plastics, rubbers, fibers or resins that have unique properties like flexibility or strength which make them suitable for various applications.
Now let’s dive into one particular polymer that stands out as the most common: polyethylene (PE). As a child playing with my colorful toys made from this material was just scratching at its surface; little did I know how much it would impact my future career path!
Most Common Polymer: Polyethylene

Polyethylene is the most common polymer in the world, with an estimated production of over 100 million metric tons per year. This versatile material is used in everything from plastic bags and food packaging to water pipes and insulation.
Polyethylene’s popularity can be attributed to its unique properties, including its low cost, high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent chemical resistance, and ease of processing.
In fact, polyethylene has become so ubiquitous that it’s hard to imagine a world without it. From the moment we wake up until we go to bed at night – we interact with products made from this amazing polymer every day.
But what makes polyethylene such an essential material in construction? Well for starters – it’s incredibly durable! Polyethylene pipes are commonly used for underground water supply lines because they’re resistant to corrosion and have a long lifespan compared to other materials like copper or steel.
Polyethene sheets are also widely used as vapor barriers under concrete slabs or foundations since they prevent moisture from seeping into buildings which could lead mold growth or structural damage over time.
Overall there’s no denying that polyethene plays a vital role not only in our daily lives but also within various industries like construction where durability matters most!
Types of Polyethylene (PE)

Polyethylene (PE) is a type of polymer that is widely used in the construction industry due to its excellent strength, durability, and resistance to chemicals. There are several types of polyethylene available on the market today, each with unique properties that make them suitable for different applications.
The most common type of polyethylene is high-density polyethylene (HDPE), which has a high strength-to-density ratio and can withstand extreme temperatures. HDPE pipes are commonly used in water supply systems because they’re resistant to corrosion and have low friction coefficients.
Another popular form of PE is low-density polyethylene (LDPE), which has more flexibility than HDPE but lower tensile strength. LDPE films are often used as protective covers for buildings during construction or as vapor barriers under concrete slabs.
Linear low-density polyethylene (LLDPE) combines the best qualities from both HDPE and LDDE – it’s flexible like LDDE but also strong like HDDE. LLDDE films find use in roofing membranes or pond liners where flexibility combined with toughness makes them ideal materials.
While there may be many types of polymers out there competing for attention; Polyethene stands out as one material that dominates our daily lives due to its versatility across various industries including construction where it finds numerous uses thanks largely because we have been able to create different forms tailored towards specific needs such as those mentioned above: High-Density Polyethene(HDPP), Low-Density Polyethene(LDPF) & Linear Low Density Polythene(LLDP).
Properties and Applications
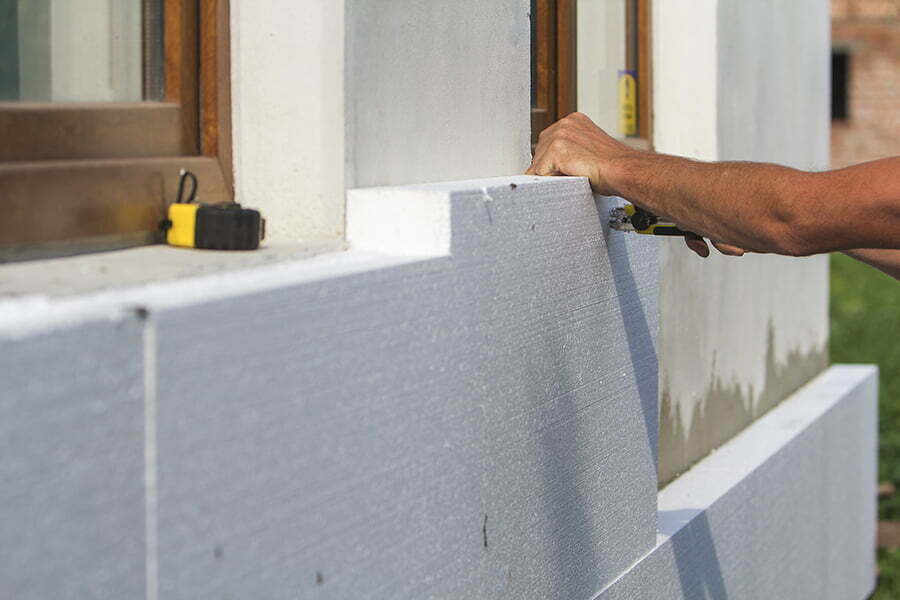

Polyethylene is a polymer that has become ubiquitous in our daily lives. It’s used to make everything from plastic bags and food containers to pipes and insulation materials.
One of the reasons for its popularity is its unique properties, which make it an ideal material for many applications.
Polyethylene is lightweight, durable, and resistant to moisture, chemicals, and UV radiation. These properties make it an excellent choice for packaging materials as well as outdoor products like playground equipment or garden furniture.
In the construction industry specifically, polyethylene plays a crucial role in providing insulation against heat loss or gain in buildings. It’s also commonly used as a vapor barrier under concrete slabs or foundations to prevent moisture from seeping through.
Moreover, polyethylene can be easily molded into different shapes using various manufacturing techniques such as extrusion molding or blow molding processes making it versatile enough for use across multiple industries including automotive parts production where they are used extensively due their durability characteristics.
Overall Polyethene stands out among other polymers because of its versatility making it one of the most widely produced plastics globally with over 100 million tons being produced annually according to recent statistics by Plastics Europe (2019).
Manufacturing Process
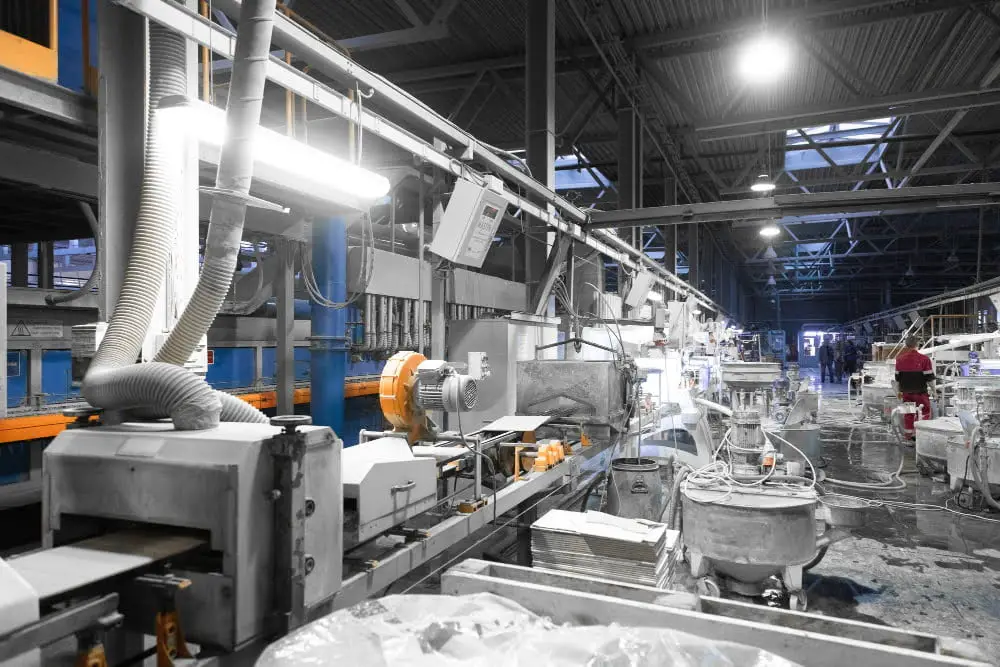

Polyethylene is a polymer that is widely used in the construction industry due to its durability, flexibility, and resistance to moisture. But how exactly is it made? The manufacturing process for polyethylene involves several steps.
Firstly, ethylene gas (a hydrocarbon) is produced from crude oil or natural gas. This ethylene monomer then undergoes a process called polymerization where it’s combined with other monomers to form long chains of polyethylene molecules.
The type of polyethylene produced depends on the conditions under which the reaction takes place – specifically temperature and pressure. High-density polyethylene (HDPE), for example, requires high pressure and temperatures up to 300°C while low-density polyethylene (LDPE) can be produced at lower pressures and temperatures around 100-150°C.
Once the polymerization process has been completed, any unreacted monomers are removed through various purification methods such as washing or vacuum stripping. The resulting product can then be molded into different shapes using techniques like extrusion or injection molding depending on its intended use.
There are many types of polymers out there each with their unique properties. Polyethene stands out as one of the most common ones due to its versatility in applications across industries. This includes construction where it plays an essential role in creating durable structures that withstand harsh environmental conditions over time!
Environmental Impact & Recycling
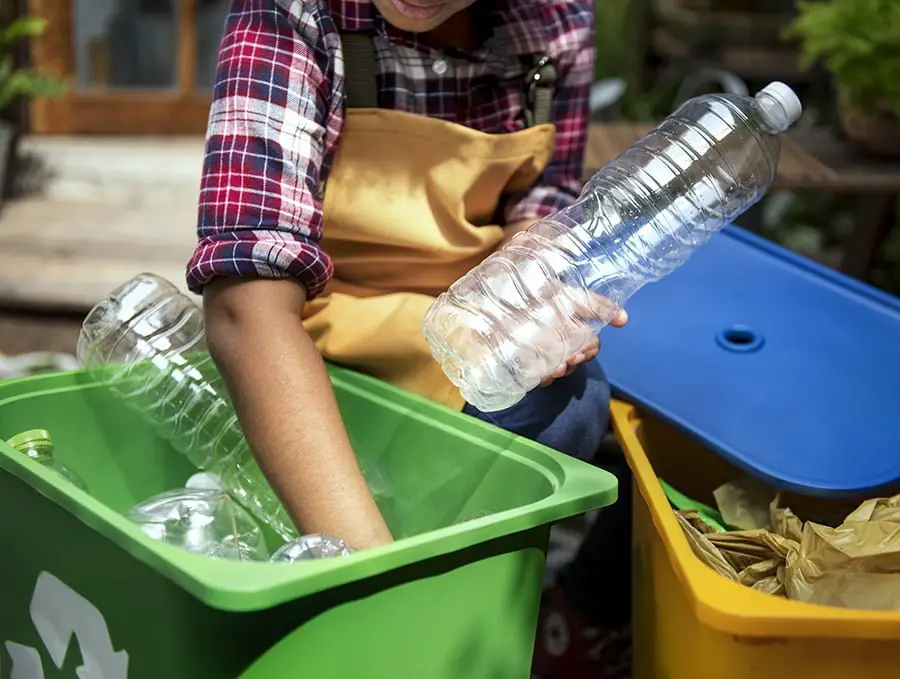

While polyethylene is undoubtedly a useful material, it’s not without its drawbacks. One of the biggest concerns surrounding this polymer is its environmental impact.
Polyethylene takes hundreds of years to decompose naturally, which means that discarded plastic products can linger in landfills and oceans for centuries.
Fortunately, there are ways to mitigate the negative effects of polyethylene on our planet. Recycling is one such solution – by reusing old plastic products instead of creating new ones from scratch, we can reduce waste and conserve resources.
In fact, many construction companies have started incorporating recycled polyethylene into their building materials as a way to promote sustainability. By using recycled plastics in place of virgin materials like wood or concrete, builders can help reduce greenhouse gas emissions and minimize their carbon footprint.
While there are certainly challenges associated with using polymers like polyethylene in construction projects (and beyond), it’s clear that these materials will continue to play an important role in our daily lives for years to come – so long as we take steps towards responsible use and disposal practices along the way!
Comparing Polyethylene With Other Common Polymers
Polyethylene is one of the most common polymers used in various industries, including construction. When comparing it with other common polymers, such as polypropylene and PVC (polyvinyl chloride), there are some key differences to consider.
Polyethylene stands out for its excellent chemical resistance and durability. It can withstand harsh environmental conditions, making it ideal for outdoor applications like pipes, cables, and roofing materials.
Polyethylene has a low coefficient of friction which makes it suitable for use in liners or coatings that require reduced frictional resistance.
On the other hand, polypropylene offers higher stiffness compared to polyethylene while maintaining good impact strength. This makes it a preferred choice when rigidity is required in applications like automotive parts or packaging materials.
PVC possesses unique properties such as flame retardancy and electrical insulation capabilities that make it widely used in building products like window frames and electrical wiring insulation.
Each polymer has its own advantages depending on specific requirements within different industries.
Innovative Uses of Polyethylene in Modern Construction
Its unique properties make it an ideal choice for various construction projects.
One notable use of polyethylene is in geomembranes. These are impermeable liners made from high-density polyethylene (HDPE) that are used to contain liquids or gases.
Geomembranes play a crucial role in preventing leaks and protecting the environment by acting as barriers for landfills, wastewater treatment ponds, and hazardous waste containment sites.
Another innovative application of polyethylene is its use as insulation material. Polyethylene foam insulation provides excellent thermal resistance while being lightweight and easy to install.
It helps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures by reducing heat transfer through walls, roofs, floors, and pipes.
Polyethylene pipes have also revolutionized plumbing systems due to their durability and corrosion resistance properties. They can withstand extreme temperatures without cracking or deteriorating over time like traditional metal pipes might do.
In addition to these uses mentioned above, polyethylene can be found in roofing membranes that provide weatherproofing protection against water infiltration; it is also utilized as a protective coating on wires for electrical installations due to its insulating capabilities.
Health Risks and Safety Measures Related to Polyethylene
It is important to be aware of potential health risks and take necessary safety measures when working with this material.
One primary concern associated with polyethylene is its flammability. When exposed to high temperatures or open flames, polyethylene can melt and release toxic fumes that may pose a risk to human health.
Therefore, it is crucial to handle and store polyethylene products away from heat sources or potential ignition points.
Another aspect worth considering is the potential for skin irritation caused by prolonged contact with certain forms of polyethylene such as powders or fibers. It’s advisable to wear appropriate protective clothing like gloves and goggles when handling these materials directly.
Furthermore, during manufacturing processes involving high temperatures or chemical reactions (such as recycling), there might be a possibility of releasing hazardous substances into the environment if proper precautions are not taken. This highlights the importance of adhering strictly to safety guidelines provided by manufacturers while using equipment like extruders or injection molding machines.
To mitigate any risks associated with working around polyethylene products in construction settings:
- Ensure adequate ventilation in work areas where melting or processing takes place.
- Follow recommended storage conditions specified by manufacturers.
- Use personal protective equipment (PPE), such as gloves and masks when required.
- Educate workers about proper handling techniques specific to different forms of polyethylene they encounter on-site.
- Regularly monitor air quality levels within enclosed spaces where large amounts of plastic are being processed.
Advancements in Polyethylene Recycling Technologies
Recent advancements in recycling technologies have shown promising results in addressing this issue.
One notable advancement is the development of advanced sorting techniques that can effectively separate different types of polyethylene based on their chemical composition and properties. This allows for more efficient recycling processes and ensures that each type of polyethylene is recycled appropriately.
Another breakthrough is the introduction of innovative mechanical recycling methods. These methods involve shredding or melting down waste polyethylene products to create new materials with similar properties as virgin plastic.
This not only reduces waste but also conserves valuable resources by minimizing the need for producing new plastic from fossil fuels.
Chemical recycling has also emerged as a viable solution for tackling polyethylene waste. Through various chemical processes such as depolymerization or pyrolysis, used polyethylene can be broken down into its basic building blocks or converted into other useful chemicals and fuels.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring biodegradable alternatives to traditional non-biodegradable forms of polyethylenes like high-density (HDPE) and low-density (LDPE). These biodegradable versions offer an environmentally friendly option while still maintaining many desirable characteristics found in conventional plastics.
The Future of Polyethylene: Biodegradable Alternatives
In response to this need, researchers and scientists have been developing biodegradable alternatives that can potentially replace polyethylene in various applications.
One promising option is polylactic acid (PLA), which is derived from renewable resources such as corn starch or sugarcane. PLA has similar properties to polyethylene but offers the added benefit of being compostable under specific conditions.
It can be used in packaging materials, disposable cutlery, and even 3D printing filaments.
Another alternative gaining attention is polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA). PHA polymers are produced by bacteria through fermentation processes using organic waste materials as feedstock.
These biopolymers exhibit excellent biodegradability and have potential applications in agriculture films, food packaging, and medical devices.
Furthermore, researchers are exploring other innovative approaches such as blending natural fibers with bio-based resins to create composite materials that possess both strength and sustainability. These composites could find use in construction components like insulation boards or structural elements.
While these biodegradable alternatives show promise for reducing environmental impact compared to traditional plastics like polyethylene; further research on their performance characteristics including durability under different conditions will be crucial before widespread adoption occurs.
FAQ
What is the most common type of polymer?
The most common type of polymer is High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE).
What are 3 common polymers?
Three common polymers are nylon (a synthetic polymer), cellulose (a naturally occurring polymer), and polyester (another synthetic polymer).
What is the most commonly used polymer plastic?
The most commonly used polymer plastic is Polyethylene Terephthalate, also known as PET or PETE.
What are most polymers?
Most polymers, whether natural or synthetic, are known as copolymers as they are composed of two or more different types of monomers.
How are polymers incorporated into building materials in the construction industry?
Polymers are incorporated into building materials in the construction industry often as adhesives, sealants, insulation, coatings, and decorative finishes due to their durability, flexibility, water resistance, and enables enhanced energy efficiency.
What are the advantages of using polymer-based materials in construction?
Polymer-based materials offer numerous advantages in construction including durability, versatility, cost-effectiveness, resistance to corrosion, and exceptional thermal and sound insulation abilities.
What are the potential environmental impacts of using polymers in construction?
The use of polymers in construction can lead to increased environmental impacts such as non-biodegradable waste accumulation, greenhouse gas emissions during production, and potential leaching of toxic substances.
Recap




