Discover how metal building vents play a crucial role in maintaining the structural integrity of your property because they significantly contribute to air circulation, control humidity, and prevent condensation-related damage.
Key takeaways:
- Metal building vents regulate temperature and control moisture.
- Good ventilation extends the lifespan of metal buildings.
- Vents improve air quality and provide comfort for occupants.
- Different types of vents serve specific purposes in metal buildings.
- Climate and geographic location impact ventilation requirements.
Understanding Ventilation Needs in Metal Buildings

Ventilation serves multiple purposes in metal buildings, from maintaining air quality to controlling temperature and humidity. The size of the building, its geographic location, and the purpose it serves dictate the extent of ventilation required.
Here are some key points to consider:
- Temperature Regulation: Metal buildings can become very hot or cold due to their conductive nature. Proper ventilation helps stabilize internal temperatures by allowing hot air to escape and cooler air to enter.
- Moisture Control: Metal buildings are prone to condensation when warm, moist air comes into contact with cooler surfaces. Ventilation helps reduce moisture levels, protecting the structure from corrosion and mold.
- Air Quality: Activities within metal buildings, such as woodworking or painting, can deteriorate the air quality. Ventilation ensures a regular exchange of air, removing contaminants and providing fresh air.
- Prolonging Building Life: Good ventilation extends the building’s lifespan by preventing rust, corrosion, and other moisture-related damages.
- Enhancing Comfort: For occupied metal buildings, ventilation contributes to a more comfortable environment by reducing odors and providing fresh air.
Understanding these points is vital in designing an effective ventilation system tailored to a specific metal building’s requirements.
Types of Vents for Metal Buildings
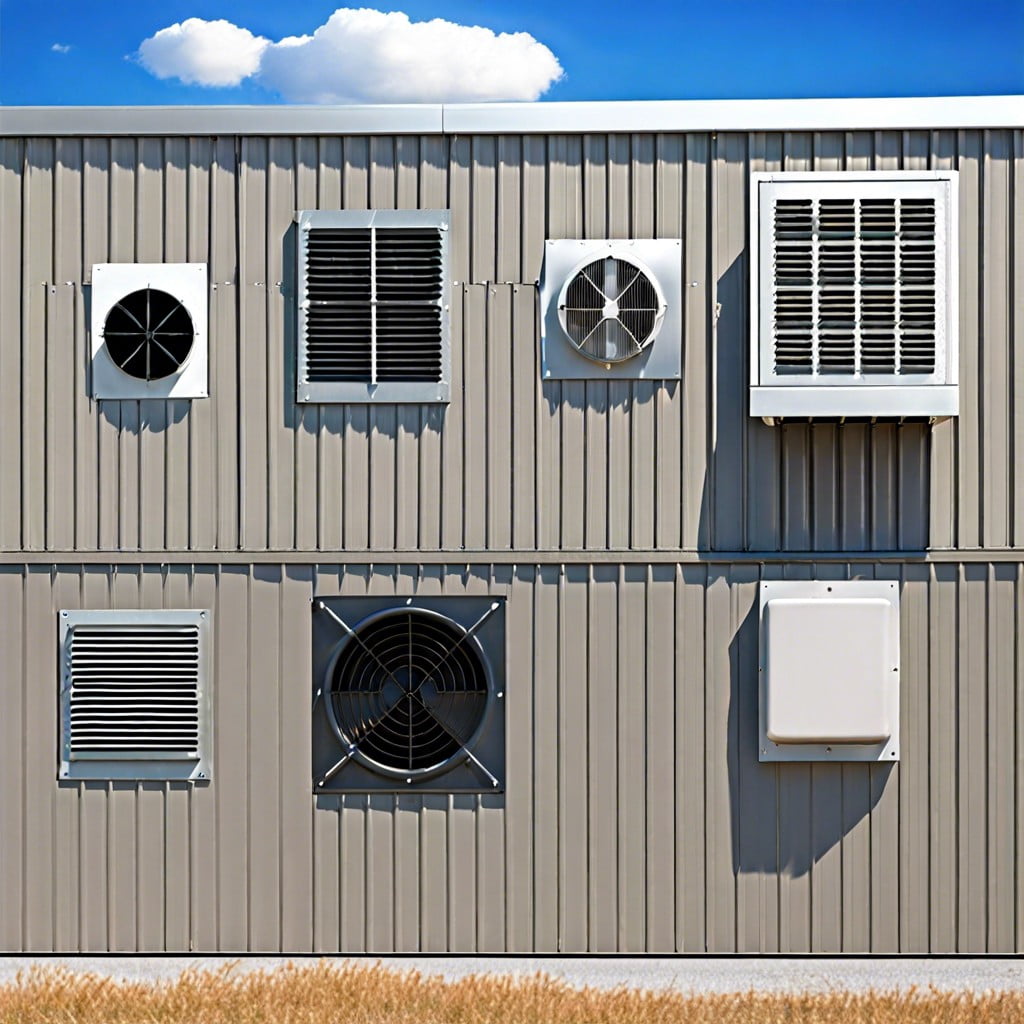
Metal buildings benefit from a variety of ventilation options tailored to specific requirements:
- Louvered Vents: These fixed or adjustable slats permit airflow while blocking direct light and rain, making them ideal for wall installations.
- Ridge Vents: Positioned at the peak of the roof, these vents allow hot air to escape naturally, promoting continuous air movement along the roofline.
- Turbine Vents: Also known as whirlybirds, these wind-driven vents spin to draw out hot, stale air from the attic space, improving circulation.
- Gable Vents: Installed on the building’s gable ends, these vents encourage cross-ventilation by allowing air to enter at one end and exit at the other.
- Soffit Vents: Commonly used in conjunction with ridge or gable vents, soffit vents are placed in the eaves to provide fresh air intake for the attic.
- Overhead Door Vents: These vents fit into the spaces above or within large doors to facilitate airflow even when doors are closed.
- Wall Vents: Positioned strategically on side walls, these can be simple openings or fitted with fans for forced air movement.
- Foundation Vents: These help control moisture levels in crawl spaces and are crucial in regions with high humidity.
- Cupolas: Serving a dual purpose, cupolas add a decorative element as well as a functional ventilation path at the building’s apex.
- Door Louvers: They allow for increased air movement through door cutouts without compromising security.
Selecting the appropriate type hinges on the building’s use, size, and location to ensure effective and efficient ventilation.
The Role of Ventilation in Preventing Condensation
Metal buildings are predisposed to condensation issues due to the difference in temperature between the interior and exterior environments. Ventilation plays a pivotal role in minimizing this effect.
- By allowing air to circulate, vents help equalize the inside and outside temperatures, reducing the likelihood of condensation.
- Proper airflow removes moisture-laden air before it can condense on cooler metal surfaces.
- Sufficiently venting a building also prevents the accumulation of stagnant air, which can be high in humidity and contribute to condensation.
- Utilizing vents in conjunction with insulation creates a barrier against temperature extremes, further mitigating condensation risks.
- Strategic placement and sizing of vents ensure optimal performance without compromising the building’s integrity or energy efficiency.
Incorporating effective ventilation techniques is essential to maintaining the structural health of a metal building by preventing the damaging effects of condensation.
Importance of Maintaining Good Air Quality in Metal Buildings
Consistent, adequate ventilation is crucial to offset the buildup of harmful pollutants, often exacerbated in metal structures due to their relatively airtight nature compared to buildings made of more porous materials. With a range of activities from industrial operations to simple storage, maintaining good air quality is essential for several reasons:
- Health and Safety: Poor air quality can lead to significant health issues for occupants, including respiratory problems and headaches. Providing fresh air through effective ventilation systems is essential for the well-being of any workers or visitors.
- Equipment Longevity: Many types of machinery and electronics function best in environments with controlled humidity and clean air. Removing airborne particles and moisture extends the life and reliability of equipment housed within metal buildings.
- Product Integrity: In cases where a metal building is used to store goods, consistent air quality ensures that products, especially those sensitive to air quality, are not compromised during storage.
- Compliance with Regulations: Occupational health and safety regulations often stipulate air quality standards that must be met. Adequate ventilation helps ensure compliance and avoids potential fines or legal issues.
- Energy Efficiency: While ventilation is generally associated with air exchange, it also plays a role in thermal comfort and energy expenditure. Implementing smart ventilation solutions contributes to reducing heating and cooling costs.
By prioritizing air quality through the strategic use of vents, metal building owners can safeguard health, preserve the integrity of stored items, and reduce energy consumption.
Comparing Natural Ventilation and Active Ventilation Systems
Natural ventilation relies on wind and thermal buoyancy to circulate air through designed openings like windows, doors, and louvers. This method is cost-effective and sustainable, as it consumes no energy from mechanical devices. It’s particularly effective in areas with steady wind patterns and mild climates where extreme temperatures aren’t a concern.
Active ventilation systems, on the other hand, utilize powered fans and blowers to control airflow. These systems offer precise regulation of air exchange rates and are essential for tightly sealed buildings, large structures, or environments requiring consistent removal of fumes, dust, or heat. Although they represent a higher initial investment and operational cost due to energy use, they provide a solution where natural forces alone are insufficient to maintain air quality and comfort.
Utilizing Louvers for Controlled Airflow
Louvers provide a means of managing airflow without the use of power-driven devices. They are installed into walls or roofs and consist of angled slats designed to let air in while keeping out unwanted elements such as water and debris. By permitting natural air movement, louvers help to balance indoor and outdoor air pressure, leading to improved ventilation.
Their adjustable mechanisms allow for fine-tuned control over air entry, which is vital for areas that require consistent airflow to manage temperature and humidity levels. Furthermore, louvers can contribute to energy savings by reducing the reliance on mechanical ventilation systems during favorable weather conditions.
In the selection process, it’s important to consider the size and design of the louvers to ensure they match the building’s ventilation requirements. The right type of louver, positioned correctly, can effectively contribute to the overall ventilation strategy, providing a simple yet effective solution to control airflow in metal buildings.
Benefits of Turbine Vents in Metal Structures
Turbine vents, often known as whirlybirds, are a popular choice for enhancing air circulation in metal buildings. These non-powered vents use wind energy to draw warm, humid air upwards and out, capitalizing on the natural principle of convection. The rotational movement of the turbine creates a vacuum, effectively pulling air from the inside of the building.
Key advantages include:
- Energy Efficiency: Operating without electricity, these devices provide cost savings by harnessing natural wind power to maintain airflow.
- Durability: With rugged metal construction, turbine vents withstand severe weather conditions and provide long-term service with minimal maintenance.
- Easy Installation: These vents can be installed quickly on the building’s roof without the need for complex machinery or extensive modifications.
- Moisture Control: By efficiently removing damp air, turbine vents help in reducing the risk of condensation-related issues, such as mold growth and structural corrosion.
Turbine vents work effectively in tandem with other ventilation components, ensuring a comprehensive system that maintains a healthy atmosphere and prolongs the lifespan of metal buildings.
Efficiency of Ridge Vents in Metal Building Roofs
Ridge vents sit at the peak of a metal building’s roof, capitalizing on the principle that hot air naturally rises. This positioning allows for a continuous release of warm air from the structure, reducing the strain on cooling systems and promoting energy efficiency.
Key features include:
- Unobtrusive Design: Slim and matching the roofline, they do not compromise the building’s aesthetic integrity.
- Consistent Ventilation: By running along the roof’s ridge, they provide uniform temperature regulation across the entire area.
- Moisture Reduction: The continuous flow of air helps to keep the roof’s underside dry, curtailing the potential for rust and corrosion in metal structures.
- Passive Operation: They harness natural forces to function, ensuring operation without the need for power, which saves on energy costs.
- Effortless Integration: Ridge vents can be easily incorporated during the construction phase or retrofitted to existing structures with minimal disruption.
Incorporating ridge vents contributes to a building’s longevity and sustainability while also promoting a comfortable interior environment.
Incorporating Supply and Exhaust Fans
Supply and exhaust fans serve as active components in regulating airflow within metal buildings. These fans work in tandem to maintain air circulation, offering several key benefits:
- Enhanced Air Exchange: Supply fans bring fresh air into the building while exhaust fans remove stale, contaminated, or hot air, leading to better indoor air quality.
- Moisture Control: By moving air in and out, these fans effectively manage humidity levels, thus reducing the risk of condensation which can lead to rust and structural damage.
- Temperature Regulation: In climates with extreme temperatures, the fans help to stabilize internal temperatures, providing comfort and safeguarding materials and equipment stored within.
- Customizable Solutions: Various sizes and types of fans can be tailored to the specific needs of the metal building, allowing for flexibility in design and function.
Incorporating these fans requires consideration of their placement and capacity to ensure optimal functionality. Careful calculation based on building size and purpose guides the selection process, ensuring that the system effectively supports the building’s ventilation needs.
Using Dampers for Airflow Regulation
Dampers are pivotal in fine-tuning the flow of air within metal buildings. These devices adjust easily, allowing you to regulate the volume of air passing through the ventilation system. In winter, minimizing airflow can help retain heat, while in hotter months, a more open damper facilitates greater air movement to cool the space.
Flexible control means you can adapt to the changing needs of the building’s interior environment. Having the ability to balance air pressure also prevents issues with doors slamming shut or drafts affecting temperature-sensitive work areas.
When installed in strategic locations, they can help distribute air evenly, ensuring every corner of the building gets adequate ventilation. This is particularly important in large structures where stagnant air pockets can form.
Moreover, the integration of automated damper controls can link to building management systems for a seamless, hands-off approach. These smart systems can respond to changes in interior air quality, occupancy, or humidity levels, adjusting dampers accordingly to maintain optimal conditions.
HVAC Systems for Climate Control in Metal Buildings
Incorporating Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning (HVAC) systems into metal buildings provides comprehensive climate control solutions. These systems ensure that temperatures remain consistent, enhancing comfort for occupants.
Key points to consider with HVAC systems include:
- Customization: HVAC units can be tailored to the specific size and use of the metal building, ensuring efficient energy use and adequate climate control.
- Integration: They can be integrated with existing ventilation systems to improve air quality and regulate humidity, crucial for preventing condensation and corrosion.
- Installment: Professional installation is important for optimal performance and to adhere to safety codes.
- Maintenance: Regular maintenance of HVAC systems is essential for longevity and to prevent costly repairs or system failures.
- Energy Efficiency: Advanced HVAC models with high Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratios (SEER) ratings can lead to significant savings on energy bills.
Selecting the right HVAC system requires evaluating the building’s layout, insulation, and local climate to establish the correct heating and cooling capacity needed for the space.
Impact of Climate On Ventilation Requirements
Different climates impose unique demands on a metal building’s ventilation system. In humid regions, increased airflow is necessary to deter mold and rust by keeping condensation at bay. Conversely, arid areas require less ventilation, focusing more on temperature control than moisture expulsion.
In colder climates, insulation paired with adequate ventilation is crucial to minimize heat loss while preventing ice damming on roofs. For locations with variable temperatures, a flexible ventilation system adaptable to seasonal changes ensures a stable internal environment throughout the year.
Coastal buildings face salt-laden air, necessitating corrosion-resistant vents and regular maintenance checks to preserve structural integrity. In contrast, industrial zones might demand specialized filters to address pollutant-heavy air and protect both occupants and stored goods.
By considering these climatic factors, a tailored ventilation approach can significantly enhance the functionality and longevity of a metal building.
Advantages of Proper Ventilation During Summer Heat
Effective ventilation provides a cooler and more comfortable environment for both personnel and stored materials. During peak summer temperatures, a well-ventilated metal building prevents heat accumulation, ensuring the inside temperature remains several degrees cooler than the outside. This reduces the need for air conditioning, thereby conserving energy and lowering utility costs.
A steady exchange of air also mitigates the risk of hot air pockets that can form in poorly ventilated spaces, potentially damaging electronics or other heat-sensitive equipment. Additionally, it helps to control humidity levels, which is particularly crucial in summer when high humidity can cause condensation and subsequent corrosion or mold growth in the building’s structure and contents.
Furthermore, proper airflow aids in expelling airborne contaminants and odors that can be exacerbated by high heat, ensuring a healthier environment for occupants. Through smart ventilation practices, metal buildings can maintain their structural integrity and provide a safe, efficient workspace throughout the summer months.
FAQ
What is the best vent for a metal building?
The ridge vent is the optimal choice for ventilating a metal building due to its superior airflow and aesthetic enhancement of the structure.
Does a metal building need to be vented?
Yes, every metal building needs to have an adequate ventilation system regardless of the season.
How do you add ventilation to a metal building?
Ventilation in a metal building can be achieved by installing fixtures such as fixed louvers, doors, hooded roof vents, or clamshell shaped ridge vents around the perimeter and on the roof, all equipped with dampers to limit cold air infiltration during winter.
What are the vents for large buildings?
The vents for large buildings, specifically ridge and eave vents, serve to prevent heat and moisture buildup while also intaking fresh air into the building, thereby ensuring excellent air quality throughout.
What impact do different types of vents have on the energy efficiency of a metal building?
Different types of vents, such as ridge vents, gable vents and louvre vents, can increase the energy efficiency of a metal building by facilitating effective circulation of air, thus reducing heat build-up, and decreasing the load on cooling systems.
Why does the strategic placement of vents in metal buildings make a significant difference?
The strategic placement of vents in metal buildings is significant as it enables efficient air circulation, which helps in temperature regulation, prevention of condensation, and reduction of harmful fumes, contributing to a healthier and safer environment inside the structure.
What are the factors that influence the number of vents needed in a metal building?
The number of vents needed in a metal building is influenced by factors such as the size of the building, its geographical location, the local climate, and the purpose of the building.
Recap




