Discover the step-by-step process to correctly install a vapor barrier in your metal building, ensuring its longevity and performance.
Installing a vapor barrier in a metal building is a critical step to prevent moisture-related issues such as rusting, mold growth, and insulation damage. This process involves selecting the right type of vapor barrier, preparing the building surface, and securing the barrier with the appropriate tools.
In this article, you’ll find a detailed guide that will take you through each step of the installation process. Whether you’re a seasoned builder or a DIY enthusiast, this comprehensive guide will provide you with all the essential details to ensure a successful and efficient vapor barrier installation.
Key takeaways:
- Vapor barriers prevent moisture-related issues in metal buildings.
- They contribute to the durability, energy efficiency, and comfort of the building.
- Vapor retarders are crucial in steel constructions for moisture control and insulation protection.
- Understanding the difference between vapor retarders and air barriers is important.
- Choosing the right fiberglass insulation facing is essential for moisture resistance.
Understanding the Role of a Vapor Barrier in Metal Buildings
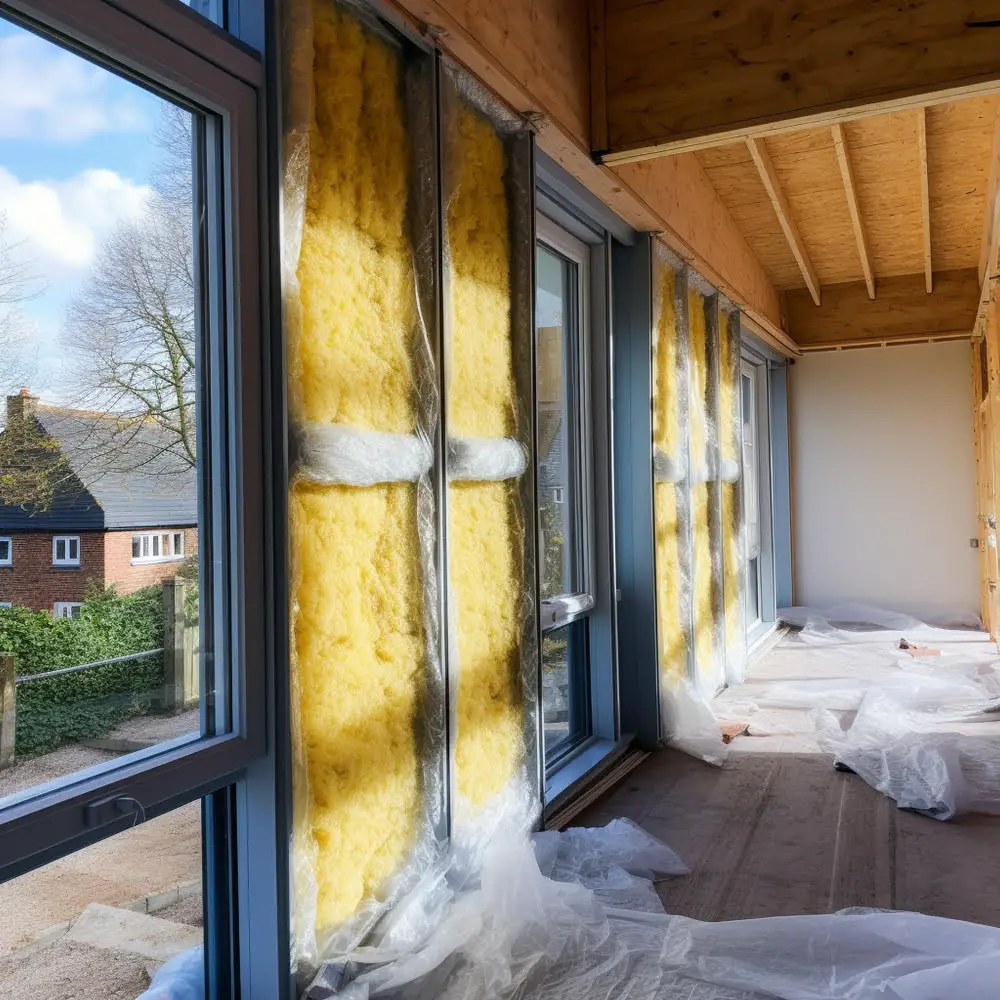

Vapor barriers, precisely known as vapor retarders, act as essential defenders against moisture infiltration. They serve the crucial role of limiting the amount of water vapor diffusing into a building where it could potentially condense into liquid water.
This function becomes increasingly important for metal buildings. Why? The fundamental reason lies in their metallic nature, which is highly conducive to changing temperatures. When the warmer interior air meets the colder metal panels, condensation risks tend to skyrocket, leading to problems like rust, corrosion, insulation damage, or even structural integrity issues.
Vapor barriers thus act to maintain the durability and longevity of your metal building. They combat moisture ingress effectively, helping to safeguard not just the insulation, but also the metal panels and other elements part of the building structure.
It’s also noteworthy to mention that these moisture barriers contribute significantly to energy efficiency. By inhibiting condensation, they help sustain a consistent indoor temperature, resulting in optimal HVAC performance and lower energy costs.
Without these vital components, moisture can cause degradation, compromise overall functionality, and shorten the lifespan of metal buildings. So, understanding their purpose is crucial when planning for any metal building project.
The Contributions of Vapor Barriers to Metal Building Efficiency
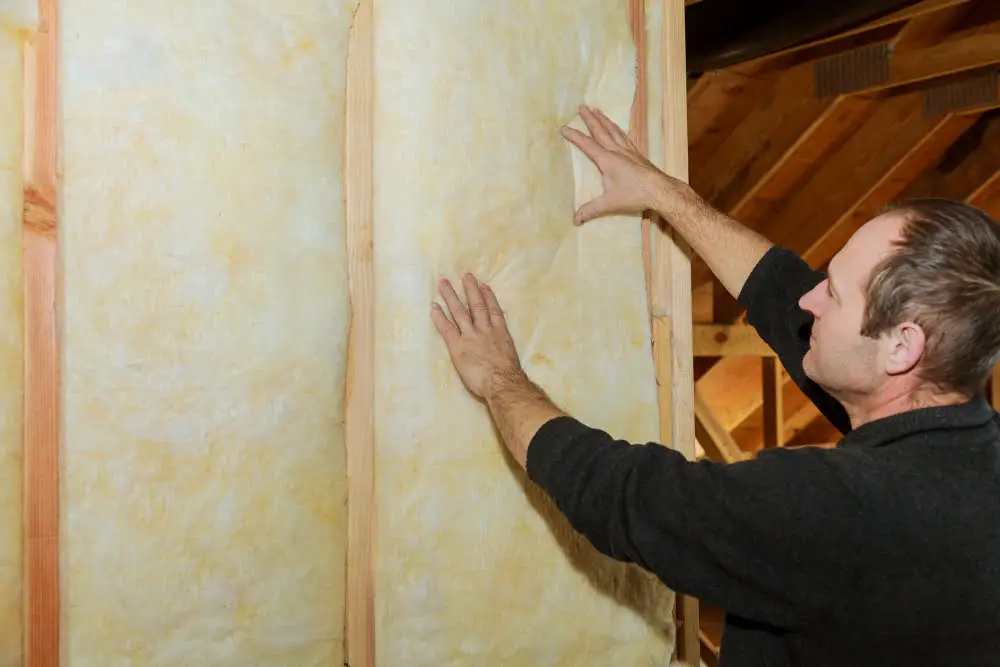

First and foremost, a vapor barrier serves as an impermeable layer that hinders the transmission of moisture, contributing to a structurally sound building. Its installation on the warm side of the insulation prevents water vapor from condensing within the interior spaces, ultimately reducing risks associated with dampness, such as mold growth or metal corrosion.
Further on, improving the longevity of metal structures isn’t the only benefit of a vapor barrier. It also significantly enhances energy efficiency. By effectively restricting air infiltration, it minimizes thermal transmission through the building sections, supporting the insulation in maintaining a desirable indoor climate. This leads to reduced energy consumption, saving on heating and cooling costs.
Lastly, a well-placed vapor barrier contributes to occupant comfort. It plays a key role in regulating humidity levels within the building. By keeping moisture from penetrating the interior spaces, it ensures a consistently comfortable environment for those within the building.
Reasoning Behind the Need for Vapor Retarders in Steel Buildings

The primary purpose of vapor retarders in steel constructions is to prevent moisture from seeping through the walls and ceiling. Their role is pivotal in maintaining the building’s thermal performance, hence ensuring energy efficiency.
1. Moisture control: They create a barrier that prevents moisture from getting inside the building. This way, the probability of condensation reduces drastically which, without a vapor barrier, can lead to rust and corrosion of metal surfaces over time.
2. Structural stability: Moisture can initiate weakening of the metal, jeopardizing the building’s integrity. A vapor retarder significantly impedes moisture entrance, contributing to the longevity of the construction.
3. Insulation protection: Insulation is vital for maintaining a comfortable indoor temperature. However, moisture can reduce its effectiveness. A vapor retarder protects the insulation material, thereby further enhancing the building’s energy efficiency.
4. Mold prevention: Excess moisture can facilitate mold growth which can lead to health issues for occupants. Vapor retarders create a safeguard against such possibilities.
It is essential, therefore, to understand that a vapor retarder in steel buildings is not just about maintaining aesthetics, but it’s more about ensuring the building’s durability and the comfort of its occupants.
Determining the Difference Between Vapor Retarders and Air Barriers
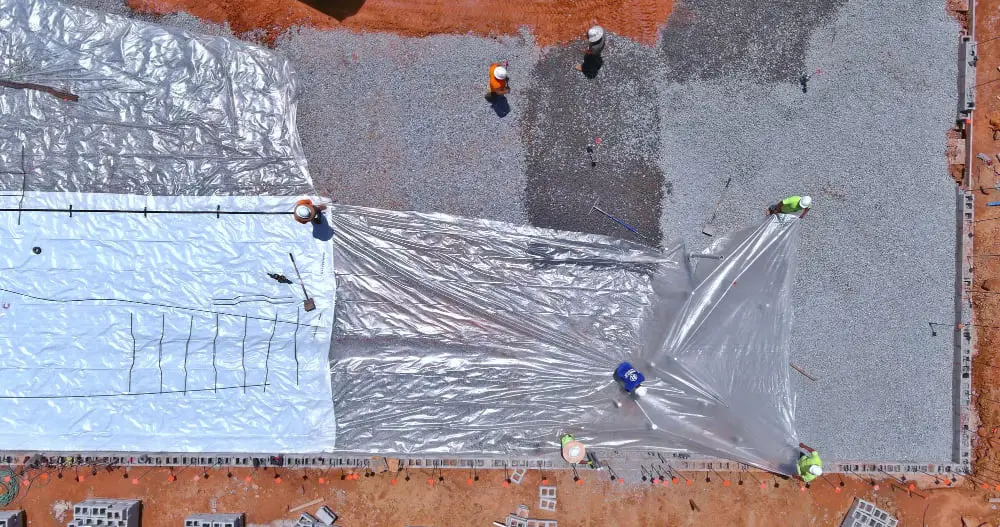

Translating technical jargon to layman’s terms, vapor retarders and air barriers are two distinct components in the context of metal building construction, each carrying a unique purpose.
Primarily, vapor retarders control the movement of moisture due to diffusion, sustaining the effectiveness of the insulation by staving off moisture content. They’re often associated with thermal envelopes, as they play a critical role in preventing condensation potential within the building assembly.
On the contrary, air barriers are designed to limit the influx of uncontrolled air through the building enclosure. By controlling air leakage, they help manage the indoor environment, prevent the distribution of pollutants, and contribute positively to the building’s energy efficiency.
There are materials available in the market that can function both as an air barrier and a vapor retarder. However, deciding which is more critical to your building’s specific needs will be a central ingredient in ensuring optimal building performance.
Guide to Selecting the Best Fiberglass Insulation Facings
When choosing fiberglass insulation facings, pay heed to the permeance levels. Lower permeance levels result in better resistance to moisture. Your selection should align with the building’s use and the local climate. Here are some factors to consider.
1. Perm Ratings: Perm ratings measure vapor diffusion. The smaller the perm rating, the better performance in retarding vapor permeance.
2. Material: Reflective aluminum foil typically forms the outer layer of most effective veneers, thanks to its moisture resistance and reflectivity.
3. Installation Challengers: Some facings are tougher to install than others. For instance, those featuring a slick reflector layer may require added attention to prevent rips during construction.
4. Tear Resistance: Look for facings that are resilient against stretching and tearing. This feature establishes the ease of installation and overall performance.
5. Flame Spread & Smoke Developed Ratings: For safety concerns, facings should have low flame spread and smoke ratings.
Ultimately, selecting the right hold facing will save the durability of your metal building and energy costs over time. As each building has specific needs, a comprehensive understanding of these factors will guide you to the correct choice for your circumstance.
Addressing Building Condensation: An Underestimated Issue
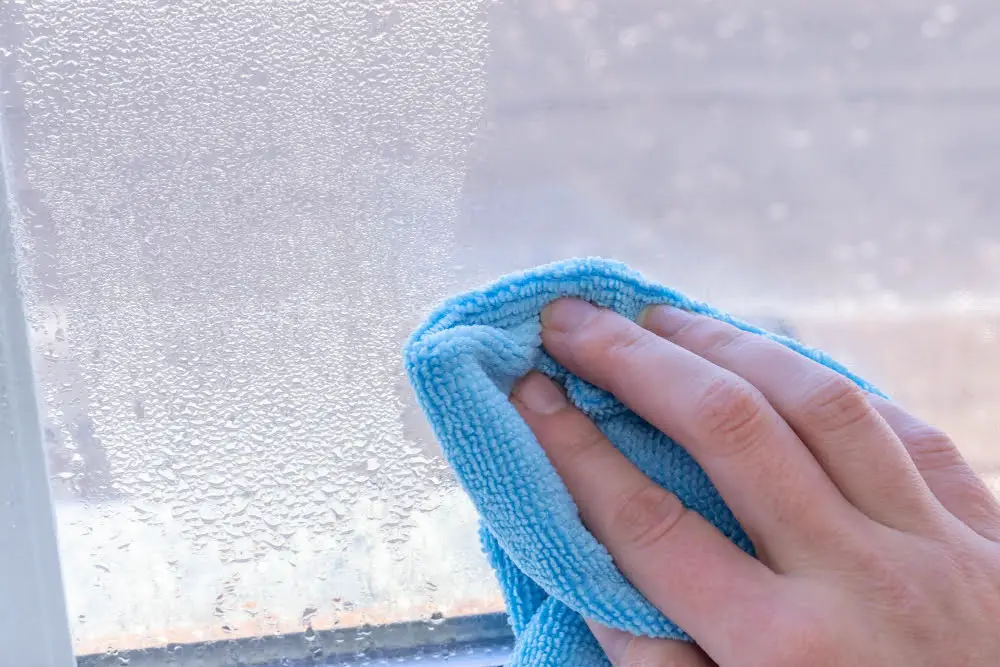

Condensation occurs when warm, humid air comes into contact with a cooler surface, leading to the formation of water droplets. For metal buildings, this typically happens when moisture-laden air from the outside reaches the cooler interior, often resulting in rust, mold, and other structural damage.
1. Problem of Moisture: Moisture acts as a catalyst for rust, leading to significant damage to metal infrastructure over time if not properly managed.
2. Mold Growth: In addition to causing rust, moisture presence aids in the flourishing of mold and mildew, leading to unhealthy indoor air quality.
3. Structural Issues: Uncontrolled condensation could result in deterioration of wooden frames or sidewalls, diminishing the building’s structural integrity.
4. Insulation Damage: Wet insulation is a poor insulator. Hence, condensation can also lead to severe thermal inefficiency.
Understanding and addressing condensation becomes critical in maintaining an efficient and durable metal building. Therefore, the application of a vapor barrier is a preventive action to keep your metal structure in optimal condition for years to come.
Prominent Benefits of Insulating Metal Buildings
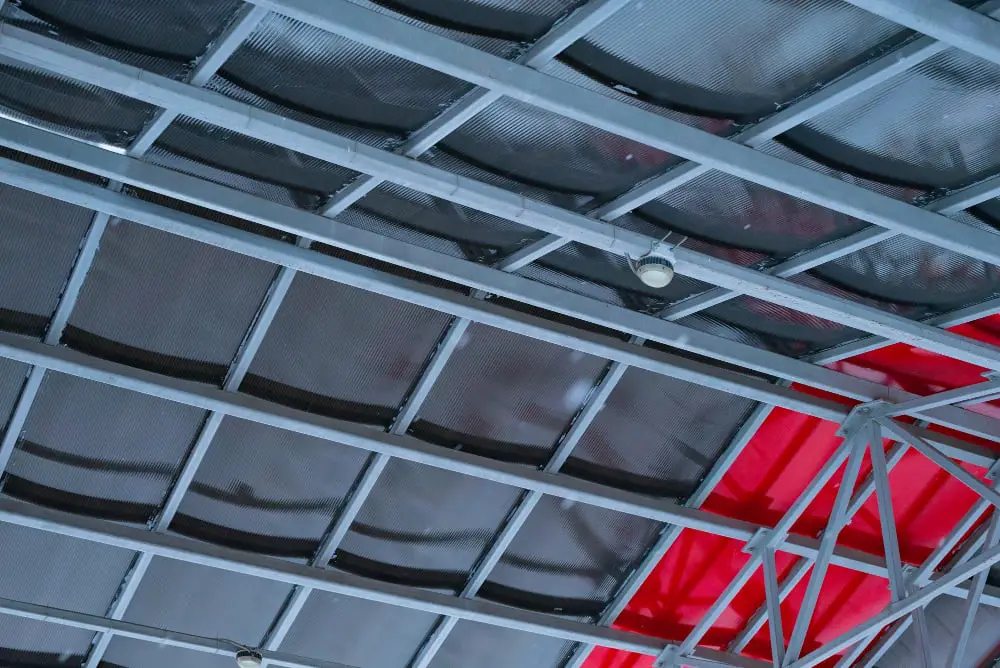

Insulation serves multiple purposes such as controlling heat flow, reducing noise, and minimizing the risk of condensation, all of which promote a more comfortable, efficient, and durable metal building.
Firstly, by controlling the flow of heat, insulation helps maintain a stable indoor temperature, reducing the need for excessive heating or cooling. This translates to substantial energy savings and decreases our environmental impact.
Secondly, insulation plays a role in noise reduction, especially useful in metal buildings which can echo and amplify sounds. This can significantly improve the comfort level in busy areas, such as workshops or commercial spaces.
Lastly, condensation can be a potential problem in metal buildings due to the properties of metal and changes in outdoor conditions. Without proper insulation, water droplets can form on the interior surfaces of your building. This can lead to corrosion, mold growth or structural damage over time. Insulation acts as a barrier, breaking the cycle of condensation and keeping your building dry and durable.
The Importance of Proper Vapor Barrier Installation

An improperly installed vapor barrier doesn’t yield the expected benefits, rendering the material and your diligent efforts ineffective. Hence, it’s crucial to maintain precision and accuracy during the installation process.
1. Maintaining Indoor Air Quality: Precision in installation can reduce vapor transmission, consequently preventing the growth of mold or mildew that can harm the building’s interior air quality.
2. Enhancing Thermal Comfort: A well-installed vapor barrier contributes to maintaining the desired indoor temperature all year round. It blocks the exterior weather-induced moisture that can otherwise disrupt thermal comfort.
3. Prolonging Building Lifespan: Moisture can expedite the corrosion process and damage the metal structure over time. Proper barrier installation safeguards the structural integrity and extends the building’s lifespan.
4. Energy Efficiency: A correctly installed barrier enables better insulation performance, reducing the energy consumption used for heating or cooling, and can lead to significant savings.
5. Compliance with Local Building Codes: Many municipalities require a vapor barrier in metal structures. A correctly installed barrier ensures your building’s compliance with local standards.
Remember, precision, accuracy, and compliance with the manufacturer’s instructions are paramount to ensuring the effectiveness of the vapor barrier.
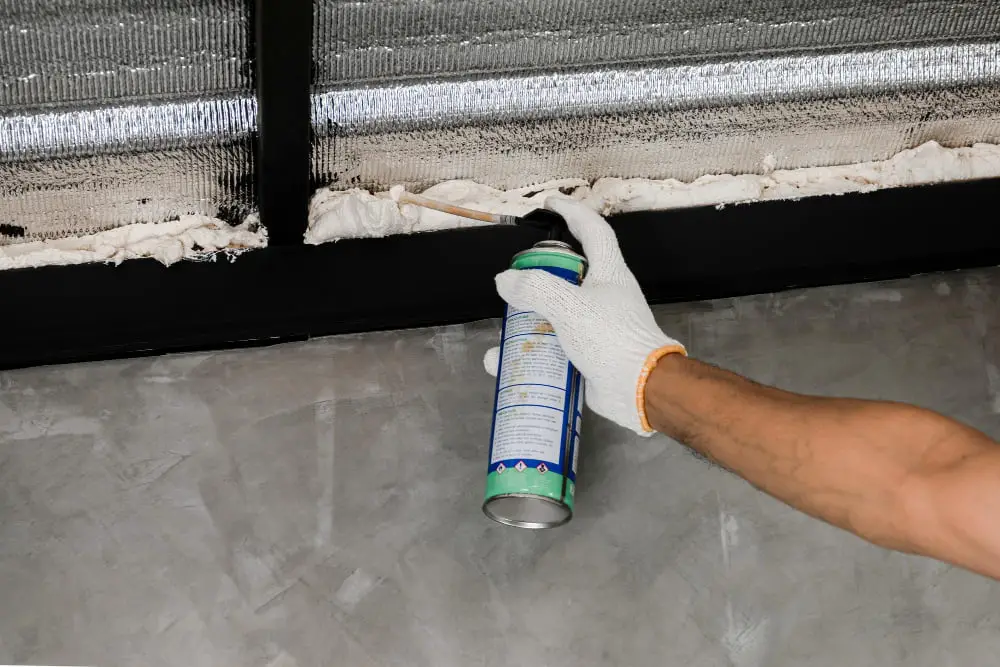
Step-by-step Procedure On Installing a Vapor Barrier in a Metal Building

Start by laying the insulation roll on the ground with the vapor barrier facing upwards. Then, unroll it along the length of the wall.
Next, cut insulation according to the lengths between columns which are typically defined by manufacturers. Using a straight edge, ensure you cut with precision.
Following that, attach the insulation to the wall girts, starting from bottom and moving upwards. The vapor barrier needs to be facing the interior of the building.
For attachment, employ the use of specific double-sided tape or banding system applicable for your metal building.
Overlap the barrier edges around four to six inches. This prevents moisture from creeping in. Sealing the overlapped area with construction tape ensures an effective seal.
The vapor barrier should extend to cover the corner columns as well. Make a slit in the barrier to allow it to overlap the next wall. Tape these edges down to form a continuous seal.
Repeat these steps until all walls are insulated. Pay close attention to ensure that there are no gaps, as this could compromise the efficiency of the barrier.
Finally, make sure to follow all safety guidelines and wear appropriate safety gear during the process. Consider consulting with a professional if you are unsure about any step.
FAQ
Where do you put a vapor barrier in a metal building?
In metal building construction, a vapor barrier is typically positioned over the purlins and under the metal roof.
Does a metal building need a vapor barrier?
Yes, a metal building requires a vapor barrier, typically provided by choosing blanket insulation with laminated facing.
How far up should a vapor barrier be installed?
A vapor barrier should be installed up the wall, extending six to twelve inches above the outside grade, and should be permanently attached and sealed to the foundation wall.
Do I need vapor barrier metal garage?
Yes, a vapor barrier is required for a metal garage to protect against condensation and ensure proper insulation.
What are the potential implications of not installing a vapor barrier in a metal structure?
Failing to install a vapor barrier in a metal structure can lead to moisture accumulation, thereby causing corrosion, structural damage, and potential mold growth.
How does climate affect the need for a vapor barrier in a metal building?
Climate significantly affects the need for a vapor barrier in a metal building as regions with high humidity or drastic temperature changes require this barrier to prevent condensation, thereby ensuring the metal building’s longevity.
What is the recommended type of vapor barrier for metal buildings and why?
The recommended type of vapor barrier for metal buildings is typically a polyethylene plastic sheeting due to its durability, water-resistant nature, and relative ease of installation.
Recap




